
A modern car is a developed electrical system with dozens of electrical appliances for various purposes. The control of these devices is based on simple devices - electromagnetic relays. Read all about relays, their types, design and operation, as well as their correct choice and replacement, in the article.
What is an electromagnetic relay?
Automotive electromagnetic relay is an element of the vehicle's electrical system; An electromechanical control device that provides closure and opening of electrical circuits when a control signal is applied from the controls on the dashboard or from sensors.
Each modern vehicle is equipped with a developed electrical system, which includes dozens, or even hundreds of circuits with various devices - lamps, electric motors, sensors, electronic components, etc. Most circuits are manually controlled by the driver, but the switching of these circuits is not carried out directly from the dashboard, but remotely using auxiliary elements - electromagnetic relays.
Electromagnetic relays perform several functions:
● Provide remote control of power circuits, making it unnecessary to pull large wires directly to the dashboard of the car;
● Separate power circuits and electrical control circuits, improving the safety and reliability of the vehicle's electrical system;
● Reduce the length of the wires of power circuits;
● Facilitate the implementation of a centralized control system for the electrical equipment of the car - the relays are assembled in one or more blocks in which a large number of electrical circuits converge;
● Some types of relays reduce the level of electrical interference that occurs when switching power circuits.
Relays are important parts of the vehicle's electrical system, incorrect operation of these parts or their failure leads to a loss of performance of individual electrical appliances or entire groups of electrical equipment, including those critical for the functioning of the car. Therefore, faulty relays should be replaced with new ones as soon as possible, but before going to the store for these parts, you should understand their types, design and characteristics.
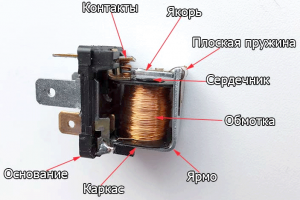
Automotive relay
Types, design and principle of operation of electromagnetic relays
All automotive relays, regardless of type and applicability, have essentially the same design. The relay consists of three main parts: an electromagnet, a movable armature and a contact group. The electromagnet is a winding of enameled copper wire of small cross-section, mounted on a metal core (magnetic core). The movable armature is generally made in the form of a flat plate or an L-shaped part, hinged above the end of the electromagnet. The anchor rests on a contact group made in the form of elastic plates with riveted bronze or other contact points. This whole structure is located on a base, in the lower part of which there are standard knife contacts, closed with a plastic or metal casing.
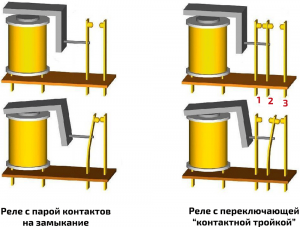
design Working principle of 4 and 5 pin relays
The connection method and the principle of operation of the relay are based on simple principles. The relay is divided into two circuits - control and power. The control circuit includes an electromagnet winding, it is connected to a power source (battery, generator) and to a control body located on the dashboard (button, switch), or to a sensor with a contact group. The power circuit includes one or more relay contacts, they are connected to the power supply and the controlled device / circuit. The relay works as follows. When the control is turned off, the electromagnet winding circuit is open and the current does not flow in it, the electromagnet armature is pressed out of the core by a spring, the relay contacts are open. When you press a button or switch, a current flows through the winding of the electromagnet, a magnetic field arises around it, which causes the armature to be attracted to the core. The armature rests on the contacts and shifts them, ensuring the closure of the circuits (or, conversely, opening in the case of normally closed contacts) - the device or circuit is connected to the power source and begins to perform its functions. When the electromagnet winding is de-energized, the armature returns to its original position under the action of the spring, turning off the device / circuit.
Electromagnetic relays are divided into several types according to the number of contacts, the type of contact switching, the installation method and electrical characteristics.
According to the number of contacts, all relays are divided into two types:
● Four-pin;
● Five-pin.
In the relay of the first type there are only 4 knife contacts, in the relay of the second type there are already 5 contacts. In all relays, the contacts are arranged in a certain order, which eliminates the incorrect installation of this device in the mating block. The difference between 4-pin and 5-pin relays is the way the circuits are switched.
A 4-pin relay is the simplest device that provides switching of only one circuit. Contacts have the following purpose:
● Two contacts of the control circuit - with their help, the winding of the electromagnet is connected;
● Two contacts of the switched power circuit - they are used to connect the circuit or device to the power supply. These contacts can only be in two states - "On" (current is flowing through the circuit) and "Off" (current is not flowing through the circuit).
A 5-pin relay is a more complex device that can switch two circuits at once. There are two varieties of this type of relay:
● With switching of only one of the two circuits;
● With parallel switching of two circuits.
In devices of the first type, contacts have the following purpose:
● Two contacts of the control circuit - as in the previous case, they are connected to the winding of the electromagnet;
● Three contacts of the switched circuit. Here, one pin is shared, and the other two are connected to the controlled circuits. In such a relay, the contacts are in two states - one is normally closed (NC), the second is normally open (HP). During the operation of the relay, switching between two circuits is carried out.
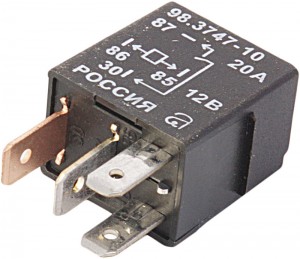
Four-pin automotive relay
In devices of the second type, all contacts are in the HP state, so when the relay is triggered, both switched circuits are immediately turned on or off.
Relays may have an additional element - an interference-suppressing (quenching) resistor or a semiconductor diode installed parallel to the winding of the electromagnet. This resistor/diode limits the self-induction current of the electromagnet winding when applying and removing voltage from it, which reduces the level of electromagnetic interference generated by it. Such relays are of limited use for switching some circuits of the automotive electrical system, but in most cases they can be replaced with conventional relays without negative consequences.
All types of relays can be mounted in two ways:
● Only installation in the counter block - the device is held by the frictional forces of the contacts in the sockets of the pad;
● Installation in the counter block with fixation with a bracket - a plastic or metal bracket for a screw is made on the relay housing.
Devices of the first type are installed in relay and fuse boxes, they are protected from falling out by a cover or special clamps. Devices of the second type are designed for installation in the engine compartment or in another place of the car outside the unit, the reliability of installation is provided by the bracket.
Electromagnetic relays are available for a supply voltage of 12 and 24 V, their main characteristics are:
● Actuation voltage (usually a few volts below the supply voltage);
● Release voltage (usually 3 or more volts less than the actuation voltage);
● The maximum current in the switched circuit (can range from units to tens of amperes);
● Current in the control circuit;
● The active resistance of the electromagnet winding (usually no more than 100 ohms).
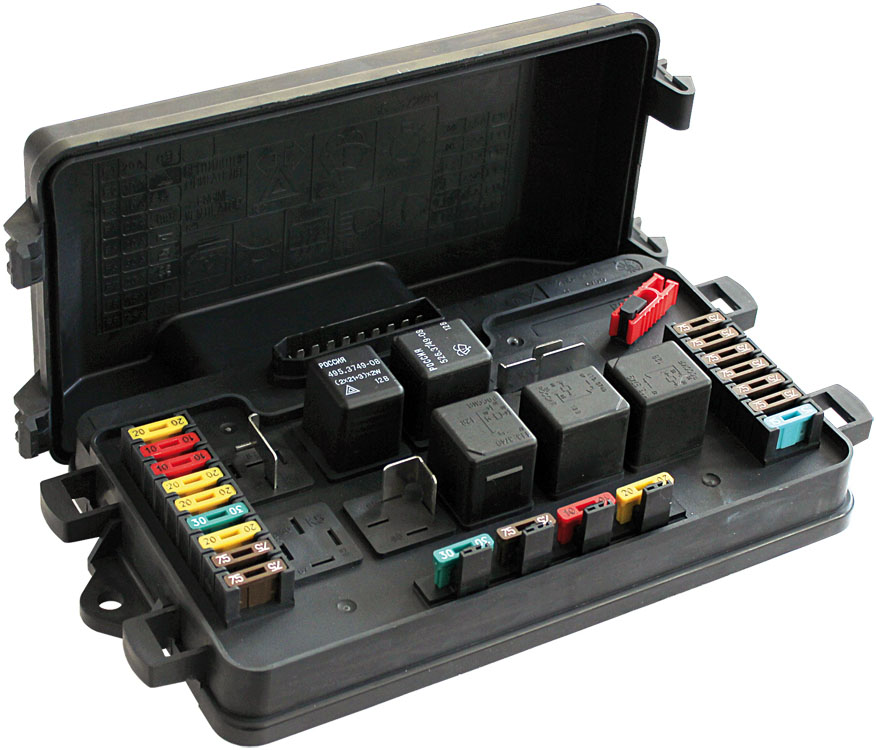

Relay and fuse box
Some characteristics (supply voltage, occasionally currents) are applied to the relay housing, or are part of its marking. Also on the case there is a schematic diagram of the relay and the purpose of its terminals (in many cases, the numbers of the pins corresponding to the numbers according to the schematic diagram of the electrical system of specific cars are also indicated). This greatly facilitates the selection and replacement of electromagnetic relays in the car.
How to choose and replace an electromagnetic relay
Automotive relays are subjected to significant electrical and mechanical loads, so they fail periodically. The breakdown of the relay is manifested by the failure of any devices or circuits of the automotive electrical system. To eliminate the malfunction, the relay must be dismantled and checked (at least with an ohmmeter or probe), and if a breakdown is detected, replace it with a new one.
The new relay must be of the same type and model as previously used. The device must be suitable in terms of electrical characteristics (power supply, actuation and release voltage, current in the switched circuit) and the number of contacts. If there was a resistor or diode in the old relay, then it is desirable that they are present in the new one. Relay replacement is performed by simply removing the old part and installing a new one in its place; If a bracket is provided, then one screw / bolt must be unscrewed and tightened. With the right choice and replacement of the relay, the electrical equipment of the car will immediately start working
Post time: Jul-14-2023
