
On most domestic cars (and on many foreign-made cars), the traditional scheme of driving the speedometer from the gearbox using a special flexible shaft is used. Read about what a flexible speedometer shaft is, how it works and how it works in this article.
What is a flex speedometer shaft?
The flexible shaft of the speedometer is an element of the drive of mechanical and electromechanical automotive speedometers. The function of the flexible shaft is to transfer torque from the secondary shaft of the gearbox to the speed unit and the speedometer odometer. Also, this part solves several technical and structural problems, for example, it ensures the normal functioning of the speedometer regardless of its position relative to the gearbox, allows you to abandon rigid gears, etc.
In the last two decades, flexible speedometer shafts have significantly lost ground to speed sensors and electronic speedometers, but flexible transmission is still widely used on inexpensive cars and the domestic auto industry. A mechanical or electromechanical speedometer with a flexible shaft drive is the easiest and cheapest way to measure speed, so it is unlikely to be completely replaced by electronic devices in the coming years.
How does the flexible shaft of the speedometer work?
The flexible shaft has a not too complicated device. The basis of the shaft is a steel cable, twisted from three, four or five layers of round wire (the cable also has a steel core, on which the wire is wound). Both ends of the cable have a square cross-section with a side of 2, 2.6 or 2.7 mm at a length of 20-25 mm - by means of a square, the cable is connected to the drive and to the speedometer.
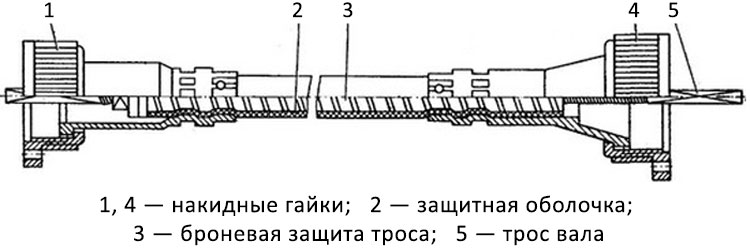
The cable is placed in armor protection (or simply armor) - a flexible tube twisted from a spirally wound metal or plastic tape. Armor protection for 2/3 of the length is filled with grease of the Litol type - this ensures its uniform rotation of the cable without jamming, as well as corrosion protection. The armor, in turn, has a protective coating made of PVC, polyethylene or oil-resistant rubber. Protective springs can be located on the shaft, as well as one or more rubber cuffs (bushings) to protect against damage to the shaft shell when passing through holes in the structural elements of the car.
At the ends of the armor protection, nipples are rigidly attached - conical parts on which union nuts are located for attaching to the gearbox and speedometer. Nuts and nipples can be made of plastic or metal. On the gearbox side, the nut has a larger size. On the same side of the cable there is a locking (expanding) washer, which rests on the shoulder inside the nipple, and prevents the longitudinal displacement of the cable inside the armor (it is also needed to service the shaft - after removing the washer, you can pull out the cable and fill the armor with grease).
The characteristics and design of flexible shafts manufactured in Russia are regulated by the GOST 12391-77 standard. In accordance with the standard, cars and motorcycles are equipped with flexible shafts of speedometers with left-hand rotation of a semi-collapsible type (with a removable cable, as mentioned above) with several types of connections from the gearbox and speedometer (as well as the shafts themselves, the connecting sockets for their installation are standardized). The length of the shafts can range from 530 mm to several meters, but the most commonly used shafts are from 1 to 3.5 meters in length.
How does a flexible speedometer shaft work?
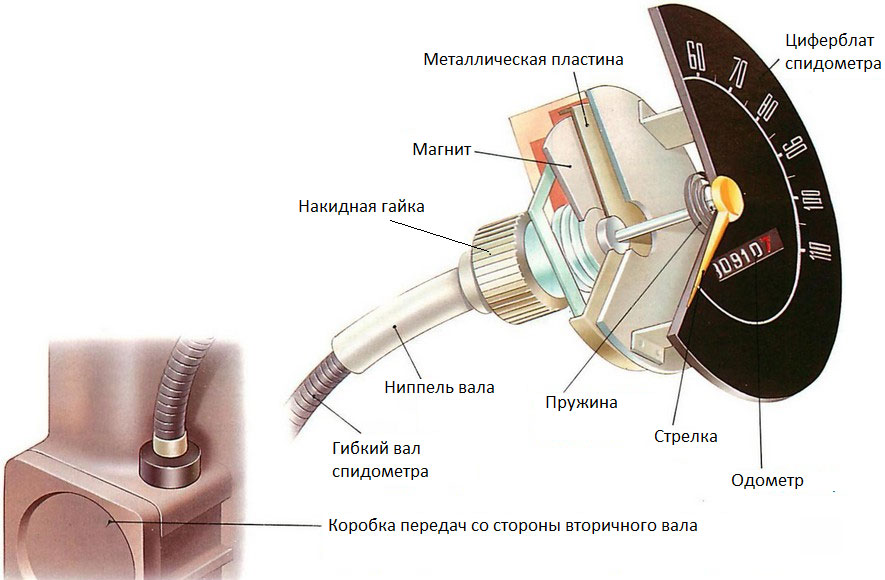
The shaft works simply. When the vehicle is moving, the torque from the secondary shaft of the gearbox is transmitted through the gear and the fastening device to the end of the shaft cable. The cable, due to its design, has high torsional rigidity (but only with left rotation, with reverse rotation it begins to unwind and can get stuck inside the armor), so when one end is twisted, it gets rotation along its entire length. Moreover, the cable rotates as a whole, so the change in the speed of rotation of the secondary shaft of the gearbox almost instantly affects the change in the rotation of the drive of the car speed sensor in the speedometer. Thus, the torque from the gear at the gearbox is constantly transmitted by the flexible shaft cable to the speedometer speed assembly, and the driver has the ability to track the speed of the car.
Over time, the cable loses its strength characteristics, its ends of a square section and sockets break (lose geometry), and require replacement. However, replacement and repair is not required too often - the resource of flexible shafts up to 2 meters long is at least 150 thousand km, longer shafts - at least 75 thousand km.
In case of wear or breakage, the flexible shaft of the speedometer needs to be replaced, and this must be done as soon as possible - the operation of a car with a non-working speedometer is prohibited by traffic rules (paragraph 7.4 of the "List of malfunctions and conditions under which the operation of the vehicle is prohibited"). And although, according to the law, a faulty speedometer cannot cause penalties, however, this breakdown makes it impossible to obtain a diagnostic card, and can cause a violation of the speed limit - and such violations are already punishable by fines and can have more serious consequences.
Post time: Aug-24-2023
