
In any gearbox, as in almost every mechanical device with rotating parts, there are rolling bearings in the amount of up to 12 or more pieces. Read all about gearbox bearings, their types, design and characteristics, as well as the correct selection and replacement of these parts in the article.
What is a gearbox bearing?
Gearbox bearing (gearbox bearing) - a part of the gearbox of automotive equipment; a rolling bearing of one design or another, acting as supports for the shafts and gears of the gearbox.
Depending on its type, the number of gears, the method of transmitting torque between the elements and the design, from 4 to 12 or more bearings of various types can be used in the gearbox. Bearings solve several problems:
● Performing the functions of a support for all or only individual shafts (in most cases - two supports for all shafts, in some boxes simpler or more complex schemes - one support for the input shaft, three supports for the secondary shaft, etc.);
● Acting as a support for gears mounted on the secondary shaft (in gearboxes with synchronized gears and free-rotating gears on the secondary shaft);
● Reduction of frictional forces in shaft and gear supports (reduction of torque losses in the transmission, reduction of heating of its parts).
The use of bearings ensures the correct installation of the moving components of the gearbox and greatly reduces the friction forces that arise between these parts. The condition and characteristics of the bearings determine the operation of the gearbox, its ability to normally transmit and change torque, and generally ensure the controllability of the vehicle. Therefore, worn and defective bearings must be replaced, and in order to make the right choice of these parts, it is necessary to understand their design, types and applicability.
Types, design and characteristics of gearbox bearings
In automobile, tractor and other transport gearboxes, standard rolling bearings of several main types are used:
● Single-row radial and angular contact balls;
● Ball double-row angular contact;
● Single-row radial rollers;
● Roller conical single-row;
● Roller needle single-row and double-row.
Each of the types of bearings has its own characteristics and applicability in gearboxes.
Single-row radial balls. The most common bearings that can be used as supports for all gearbox shafts. Structurally, it consists of two rings, between which there is a row of steel balls in the separator. Sometimes the balls are covered with metal or plastic rings to prevent loss of lubrication. Bearings of this type work best on relatively lightly loaded boxes of cars and motorcycles, but sometimes they are also found on some shafts of cargo boxes.
Single-row angular contact balls. These bearings normally perceive radial and axial loads, they are most often used as rear supports of the primary and secondary shafts, which during the operation of the gearbox can be subjected to loads directed along the axis (due to the movement of synchronizers and their emphasis in the gears). Structurally, a angular contact bearing is similar to a radial bearing, but its rings have stops that prevent the structure from collapsing under axial loads.
Ball double-row angular thrust. Bearings of this type are more resistant to high loads, so they are usually used as a rear support for the primary and sometimes intermediate shaft. By design, such bearings are similar to single-row bearings, but they use wide rings with outer stops for balls.
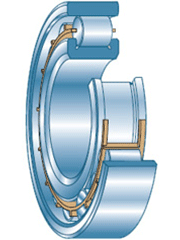
Roller single-row radial. These bearings can operate under higher loads than ball bearings, so they are used as supports for all shafts in the gearbox of automotive equipment - trucks, tractors, special equipment, agricultural machinery, etc. Structurally, bearings of this type are similar to ball bearings, but they use rollers as rolling elements - short cylinders, together with a cage, sandwiched between rings with flat inner surfaces.
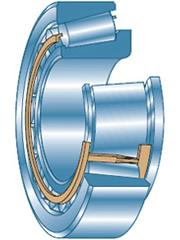
Roller conical single-row and double-row. Bearings of this type normally perceive both radial and axial loads, while they are more resistant to high loads than ball bearings. Such bearings are most often used as rear and front supports of all shafts, double-row tapered bearings are used in the rear supports of the primary and secondary shafts. The design of this bearing uses tapered rollers, which are installed between two rings with beveled inner surfaces.
Roller needle single-row and double-row. Bearings of this type, due to their design, have small dimensions with high resistance to radial loads - this is achieved by using small-diameter rollers (needles) as bodies of rotation, and sometimes additionally by abandoning rings and / or cages. Typically, needle bearings are used as gear supports on the secondary shaft, as a secondary shaft support (when its toe is located at the end of the input shaft), less often as countershaft supports.
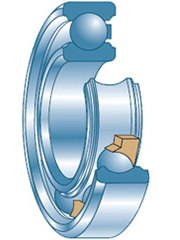

Ball bearing
Roller bearing
Tapered roller bearing
Needle double-row bearing
Gearboxes can use bearings of the same type, or many bearings of different types. For example, in KP Moskvich-2140 installed only three ball radial bearings - they hold the primary and secondary shafts, and the intermediate is installed in the box housing without rolling bearings at all. On the other hand, in the VAZ "Classic", the shafts are mostly based on deep groove ball bearings, however, a needle bearing is used in the front support of the secondary shaft, and the intermediate shaft is mounted on a roller radial (rear support) and a double-row ball bearing (front support). And in boxes with freely rotating gears on the secondary shaft, needle bearings are additionally used according to the number of gears. In each case, the designers choose those bearings that provide the best operating modes of the shafts and gears of the box, depending on the loads and operating characteristics of the unit.
All KP bearings are manufactured in accordance with standards that define the dimensions and characteristics of parts, and sometimes their production technologies and features. First of all, production is based on the GOST 520-2011 standard common to rolling bearings, and each type of bearing corresponds to its own standard (for example, conventional radial ball bearings - GOST 8338-75, needle bearings - GOST 4657-82, radial roller bearings - GOST 8328-75, etc.).
Issues of correct selection and replacement of gearbox bearings
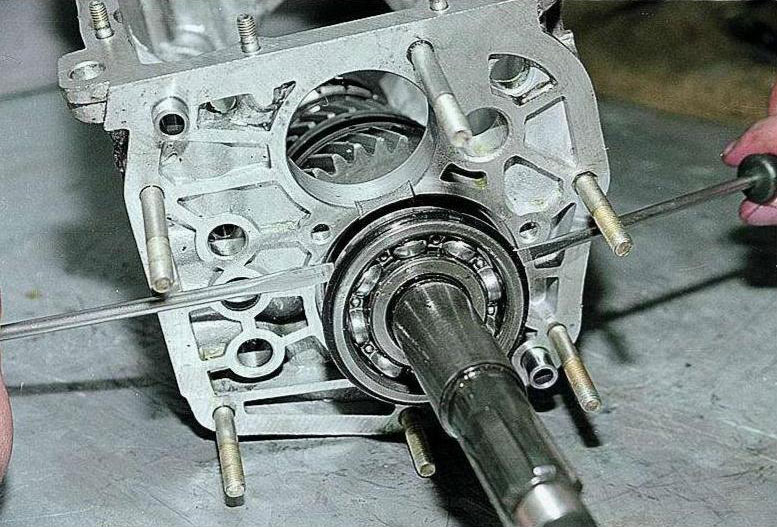
Replacement of gearbox bearings
As a rule, routine maintenance activities do not include the replacement of gearbox bearings - this is done as needed in the event of wear or destruction of parts. The need to perform such repairs can be indicated by extraneous noise and even knocks from the gearbox, spontaneous switching on and off gears, an incorrectly working or jammed clutch and, in general, a deteriorated transmission operation. In all these cases, it is necessary to make a diagnosis, and if a malfunction is detected, change the bearings.
Bearings of only those types and sizes that were installed on the box by the manufacturer should be taken for replacement. The choice of the right bearings is best done in parts catalogs or specialized reference books, which indicate the catalog numbers and types of all bearings of this particular box, as well as acceptable analogues of parts. You can buy bearings separately, but in some cases - for example, for a major overhaul of a box - it makes sense to purchase complete sets of parts for a particular model of the unit.
Replacement of bearings in most cases requires dismantling and almost complete disassembly of the gearbox (the exception is the replacement of the input shaft bearing in some gearboxes, for which the unit only needs to be dismantled from the car, but does not need to be disassembled). This work is quite complicated and requires the use of special tools (pullers), so it is better to trust it to specialists. If the repair of the box is performed correctly and in accordance with the instructions, then the unit will cease to cause problems, increasing the handling and comfort of the car.
Post time: Jul-26-2023
