In most wheeled vehicles, the wheels are held by a hub that rests on the axle through special bearings. Read all about hub bearings, their existing types, designs, features of operation and applicability, as well as the correct selection and replacement of these parts in the article.
What is a hub bearing?

Hub bearing (wheel bearing) - undercarriage assembly (wheel suspension) of wheeled vehicles; A rolling bearing of one design or another, which provides connection, alignment and free rotation of the wheel hub on the axle.
A wheel bearing performs several functions:
● Ensuring the possibility of rotation of the hub on the axle (trunnion) with minimization of friction forces;
● Mechanical connection of the hub with the axle (trunnion) or steering knuckle;
● Centering of the hub on the axis;
● Distribution of radial and lateral forces and torques transmitted from the wheel through the hub to the axle and suspension of the car, and in the opposite direction;
● Unloading the axle shafts of the drive axle - the wheel is not held on the axle shaft, but rests on the steering knuckle, trunnion or axle beam.
Wheel bearings are used to mount the hubs of all wheels of cars and trucks, buses, tractors and other equipment, steered wheels of tractors of small traction classes (usually in them the rear wheels are rigidly connected to the axle shafts), as well as in the motor-wheels of vehicles with electromechanical transmission. The hub bearing is of paramount importance for the chassis of the vehicle, so in case of any malfunctions, it must be replaced. But before making a purchase of a bearing, it is necessary to understand its types, design and features.
Types, design and features of hub bearings
Rolling bearings are used to install the hubs on the axles, which, with high strength and reliability, provide the maximum reduction in friction forces. In general, the design of the bearing is simple: these are two rings - outer and inner - between which there is a series of rolling elements enclosed in a cage (a mesh made of metal or plastic that ensures the correct location of the rolling elements). The inner space is filled with grease, the gaps between the rings are closed with covers to prevent grease leakage and contamination of the inside of the bearing. The design of different types of bearings may vary, as described below.
Wheel bearings are classified according to the design and rolling elements used, as well as the direction of the perceived load.
According to the bodies of rotation used, bearings are:
● Ball - rolling occurs on steel balls;
● Roller - rolling is carried out on conical rollers.
At the same time, according to the location of the rolling elements, bearings are divided into two groups:
● Single-row;
● Two-row.
In the first case, there is one row of balls or rollers between the rings, in the second - two rows each.
According to the normal load direction for them, hub bearings are:
● Radial-thrust;
● Radial-thrust self-aligning.
Angular contact bearings absorb forces directed both across the axis (along the radius) and along it. This ensures the normal operation of the bearing, regardless of the nature of the movement of the wheels - whether it is vibrations in the vertical plane (when driving on uneven roads), or deviations of the wheel from the longitudinal axis (turns of the steered wheels, lateral loads on the wheels when overcoming radii or when driving with a slope, side impacts on the wheels, etc.).
Due to the design, self-aligning bearings compensate for some misalignment of the axle and hub, reducing the intensity of wear of parts.
Structurally, the bearings of the types discussed above are different.
Single-row tapered angular contact bearings. They consist of two rings, between which conical rollers are sandwiched, separated by a separator. The inner space of the bearing is filled with grease, it is protected from clogging and leakage by means of an O-ring. A part of this type is non-separable.
Double-row angular contact ball bearings and self-aligning bearings. They consist of two wide rings, between which two rows of balls are staggered, separated by a common separator. Self-aligning bearings, due to the special shape of the inner surfaces of the rings, make it possible to shift the rows of balls relative to the axle of the trunnion. Conventional bearings of this type are non-separable, self-aligning - can be either non-separable or collapsible.
Double-row angular contact roller bearings. They have a design similar to the previous one. Usually, the conical rollers of each row have a mirror arrangement - a wide part of the rollers outwards. This position ensures an even distribution of loads and alignment of parts. Bearings of this type are non-separable.
Finally, wheel bearings are divided into two groups according to their design:
● Individual bearings;
● Bearings combined into one unit with a hub.
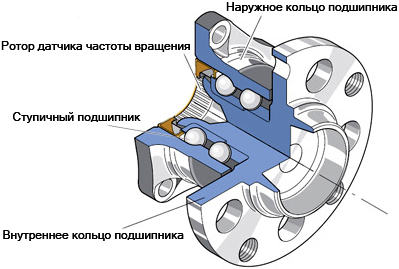
Hub with integrated double-row ball self-aligning bearing
The first type is conventional bearings, which can be installed and dismantled without replacing other mating parts. The second type is bearings integrated into the wheel hub, so they cannot be replaced separately.
Installation locations and applicability of wheel bearings
Hub bearings are divided into a number of groups according to installation location and applicability:
● Bearings of hubs of steered drive wheels (front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles);
● Bearings of hubs of steered driven wheels (rear-wheel drive vehicles);
● Bearings of the hubs of driven unsteered wheels (front-wheel drive vehicles, as well as four-axle vehicles with support non-driving axles);
● Bearings of hubs of driving uncontrolled wheels (rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive cars).
Certain types of bearings are used in various types of axles and hubs:
● In the hubs of the steered drive wheels of passenger cars - double-row ball or roller bearings;
● In the hubs of uncontrolled drive and driven wheels of passenger cars - both double-row ball or roller bearings (in most modern cars), and two tapered bearings (in many cars of early releases, including domestic ones);
● In the hubs of all wheels of all-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive commercial vehicles and trucks, buses, tractors and other equipment (with rare exceptions) there are two tapered bearings.
Mounting of bearings is carried out in various ways. On the rear wheels of front-wheel drive passenger vehicles, the hub bearing is put on the trunnion, and the hub itself or the brake drum is mounted on its outer ring. Similar components of trucks and rear-wheel drive cars have the same design, but here two bearings are installed on the axle. On the front wheels of front-wheel drive passenger cars, the bearing is mounted in the steering knuckle, and the hub is mounted in the inner ring of the bearing.
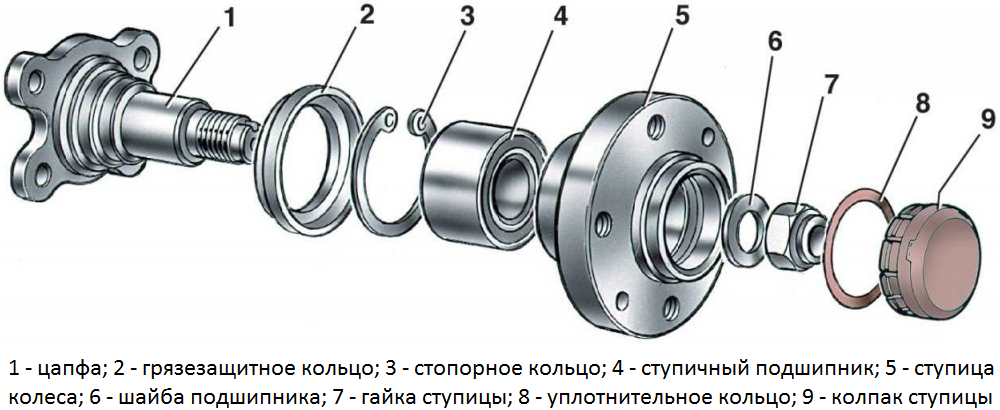
The design of the hub assembly of the rear wheels of front-wheel drive cars
Issues of selection, replacement and maintenance of the hub bearing
Wheel bearings are subjected to high loads, so they are prone to rapid wear and breakage. In cases where there is a hum of bearings, the handling of the car deteriorates, there is an unavoidable backlash of the hubs and overheating of the hub assemblies is observed, the bearings should be checked. If they are found to be worn or broken, they must be replaced.
Bearings of the types and catalog numbers that were previously installed should be selected for replacement. It is not recommended to change the type of wheel bearing, as this can change the characteristics of the chassis unpredictably. Particular attention should be paid to the choice of tapered bearings installed in pairs - in some cases they can be replaced independently of each other, in other cases only paired replacement is possible. And if the car uses hubs with integrated bearings, then you will have to buy the entire assembly assembly - a separate replacement of bearings in them is not possible.
Wheel bearings should be replaced and adjusted in accordance with the repair instructions for this car (bus, tractor), and subsequently it is necessary to carry out the maintenance measures specified in the instructions for these units. If you decide to perform the replacement yourself, you should stock up on a special tool for pressing and pressing bearings, otherwise this work will not be possible.
With proper selection and replacement, as well as regular maintenance of wheel bearings, the chassis of the vehicle will work normally in any conditions for tens of thousands of kilometers.
Post time: Aug-05-2023
