
In the transmissions of KAMAZ trucks, interaxle and cross-axle differentials are provided, in which the central place is occupied by crosses. Learn about what a cross is, what types it is, how it works and what functions it performs, as well as the selection and replacement of these parts from the article.
What is a KAMAZ differential cross?
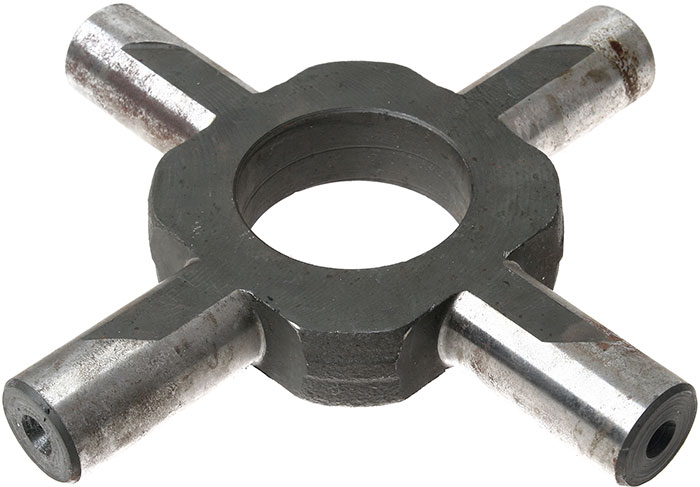
The cross of the KAMAZ differential is a part of the center and cross-axle differentials of the drive axles of KAMAZ vehicles; A cruciform part that acts as axes for satellite gears.
The cross is one of the main parts of all types of differentials - both cross-axle, located in the gearboxes of all drive axles, and inter-axle, mounted on an intermediate axle. This part has several functions:
● Acting as axles for differential satellites - gears are mounted on the spikes of the cross and rotate freely on it;
● Centering of the mating parts of the differential - satellites and gears of the axle shafts;
● Transmission of torque from the differential housing to the satellites and further to the gears of the axle shafts (in some types of these units, the torque is transmitted directly through the crosspiece);
● Uniform distribution of the load on the gears of the axle shafts - this reduces the load of all gears, increasing their service life and reliability at significant torques;
● Lubricant supply to the bushings (plain bearings) of satellites.
The condition of the cross largely depends on the operation of the differential, the efficiency of torque transmission and reliability. A faulty cross must be repaired or replaced, but before buying a new part, you should understand the types of KAMAZ crosses, their features and applicability.
Types, design and features of KAMAZ differential crosses
All KAMAZ crosses are divided into two large groups according to their applicability:
● Crosses of cross-axle differentials (drive axle gearboxes);
● Crosses of center differentials.
Crosses of the first type are used in the differentials of gearboxes of all drive axles - front, intermediate (if any) and rear. Here, this part ensures the distribution of torque between the axle shafts at uneven speeds of rotation of the right and left wheels.
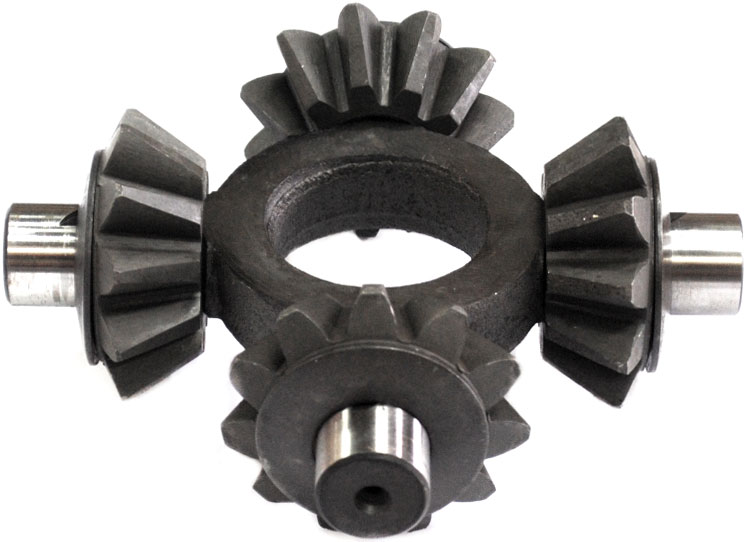

Differential cross assembly with satellites
Crosses of the second type are an integral part of center differentials installed only on intermediate drive axles of cars with wheel formulas 6×4 and 6×6, and direct transmission of torque to the intermediate and rear axles (without transfer case). Here, this part ensures the distribution of torque between the intermediate and rear axles at uneven speeds of rotation of their wheels.
Crosses of both types have the same design in principle. This is a solid part in which two parts can be distinguished: the central ring (hub), along the circumference of which four spikes are symmetrically located. The hole in the hub serves to center the part and facilitate it, and in the center differentials, the rear axle drive shaft passes through it. Satellite gears and support washers are installed on the spikes through the bushings, preventing direct contact of the satellites with the machines of the differential housing cups.
The spikes have a variable cross-section: on the sides facing the center of the crosspiece, the balds are removed in the same level with the plane of the hub of the cross. Lysks ensure the flow of oil to the bushings of the satellites and the removal of wear particles from them. Blind holes of shallow depth are usually drilled at the ends of the spikes, which facilitate the processing of the part. Also, chamfers are removed at the ends for more convenient installation of the cross in the differential housing. The diameter of the studs of the crosses of the cross-axle differentials of KAMAZ is 28.0-28.11 mm, the diameter of the studs of the crosses of the center differentials lies in the range of 21.8-21.96 mm.
All crosses are made of structural steels of grades 15X, 18X, 20X and others by hot stamping (forging) followed by turning, the surface of the studs of finished parts is subjected to heat treatment (carburizing to a depth of 1.2 mm, quenching and subsequent tempering) to achieve the required hardness and resistance to abrasive wear.
There are two types of crosses of center differentials of KAMAZ vehicles:
● With a smooth center hole;
● With slotted hub.
Parts of the first type have the design described above, they are used in center differentials, made according to the classical scheme - with the transfer of torque from the propeller shaft to the differential housing, with which the cross is rigidly connected. Parts of the second type have a hub of increased width, in the inner part of which longitudinal splines are made. These crosses are used in center differentials of a new type (installed on KAMAZ-6520 dump trucks and modifications based on them since 2009) - with the transfer of torque from the propeller shaft directly to the crosspiece. Differentials of this type are more compact and simpler, but in them the cross is subjected to higher loads, so more stringent requirements are imposed on their design and quality.
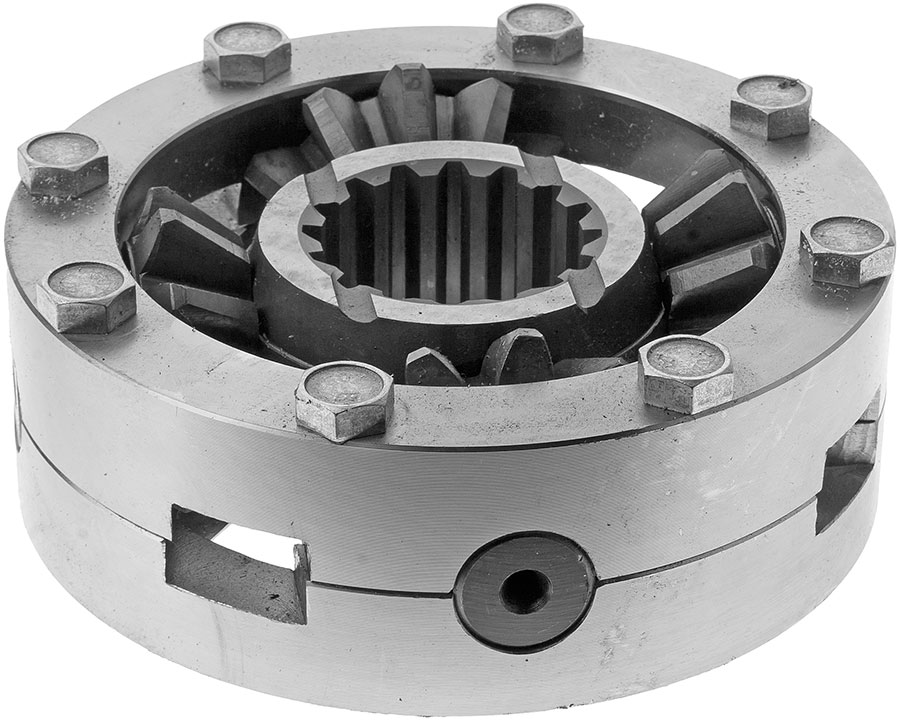

Center differential KAMAZ-6520 assembly
The operation of the D-pads in the differentials is quite simple. In the cross-axle differential, it acts only as axles for satellites. The cross is rigidly mounted between the differential housing bowls, which, in turn, is installed inside the driven gear of the main gear. When the gear rotates, the differential rotates at the same time, the satellites attached to the cross, engaged with the gears of the axle shafts, bringing them into rotation, ensuring the transmission of torque to the drive wheels. When cornering or driving on wet roads, the satellites rotate on the spikes of the crosspiece, providing different wheel speeds.
In center differentials, the crosses perform similar functions, but with their help the torque is distributed between the drive axles.
Issues of selection and replacement of crosses of KAMAZ differentials
Differential crosses are subjected to high loads during the operation of the car, so over time they wear out and deform. The condition of this part is monitored during routine maintenance or during repair of the drive axle. If chips, scuffs, cracks and other damage are found on the crosspiece, then it must be replaced. If the spikes of the cross have traces of abrasive wear with a decrease in diameter, then they can be restored by metal surfacing and grinding, but today it is much easier and cheaper to buy a new cross. If defects are detected in satellites and washers (chips, uneven tooth wear, cracks and fractures in the teeth, etc.), then they must be replaced together with the crosspiece, and a complete set (with bushings and thrust washers).
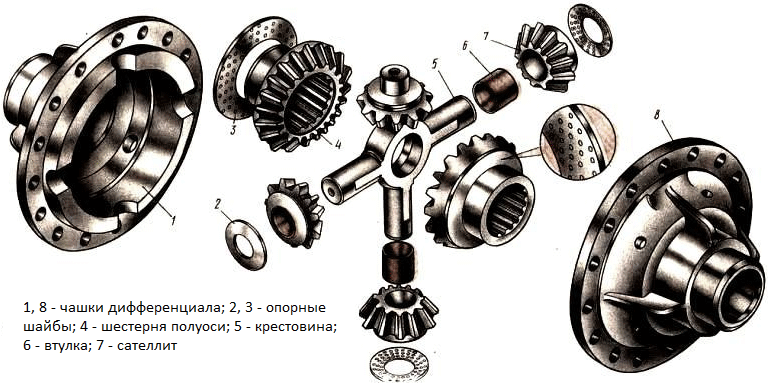
KAMAZ cross-axle differential
Differential crosses are subjected to high loads during the operation of the car, so over time they wear out and deform. The condition of this part is monitored during routine maintenance or during repair of the drive axle. If chips, scuffs, cracks and other damage are found on the crosspiece, then it must be replaced. If the spikes of the cross have traces of abrasive wear with a decrease in diameter, then they can be restored by metal surfacing and grinding, but today it is much easier and cheaper to buy a new cross. If defects are detected in satellites and washers (chips, uneven tooth wear, cracks and fractures in the teeth, etc.), then they must be replaced together with the crosspiece, and a complete set (with bushings and thrust washers).
Post time: Aug-05-2023
