
Monitoring the pressure in the lubrication system is one of the conditions for the normal functioning of an internal combustion engine. Special sensors are used to measure pressure - read all about oil pressure sensors, their types, design, principle of operation, as well as their correct selection and replacement in the article.
What is an oil pressure sensor?
The oil pressure sensor is a sensitive element of instrumentation and alarm devices for the lubrication system of reciprocating internal combustion engines; A sensor for measuring the pressure in the lubrication system and signaling its decrease below a critical level.
Oil pressure sensors perform two main functions:
• Warning the driver about low oil pressure in the system;
• Alarm about low / no oil in the system;
• Control of absolute oil pressure in the engine.
The sensors are connected to the main oil line of the engine, which allows you to monitor the oil pressure and its presence in the oil system (this also allows you to check the operation of the oil pump, if it malfunctions, the oil simply does not enter the line). Today, sensors of various types and purposes are installed on engines, which needs to be described in more detail.
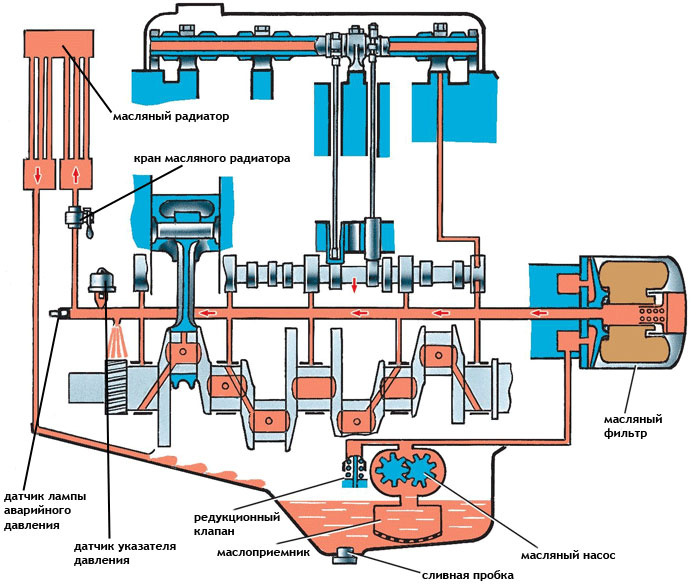
The engine lubrication system and the place of pressure sensors in it
Types, design and principle of operation of oil pressure sensors
First of all, all pressure sensors are divided into two types according to their purpose:
• Alarm sensor (alarm sensor for emergency oil pressure drop, "sensor on the lamp");
• Sensor for measuring absolute oil pressure ("sensor on the device").
Devices of the first type are used in the alarm system of a critical drop in oil pressure, they are triggered only when the pressure drops below a certain level. Such sensors are connected to sound or light display devices (buzzer, lamp on the dashboard), which warn the driver about low pressure / oil level in the engine. Therefore, this type of device is often referred to as "sensors per lamp".
Sensors of the second type are used in the oil pressure measurement system, they work over the entire pressure range in the engine lubrication system. These devices are sensitive elements of the corresponding measuring instruments (analog or digital), the indicators of which are displayed on the dashboard and indicate the current oil pressure in the engine, which is why they are often called "sensors on the instrument".
All modern oil pressure sensors are diaphragm (diaphragm). There are three main components in this device:
• Sealed cavity closed by a flexible metal membrane (diaphragm);
• Transmitting mechanism;
• Converter: mechanical signal to electrical.
The cavity with the diaphragm is connected to the main oil line of the engine, so it always maintains the same oil pressure as in the line, and any pressure fluctuations cause the diaphragm to deviate from its average position. The deviations of the membrane are perceived by the transmitting mechanism and are fed to the transducer, which generates an electrical signal - this signal is sent to the measuring device or electronic control unit.
Today, oil pressure sensors use transmission mechanisms and converters that are different in design and principle of operation, in total four types of devices can be distinguished:
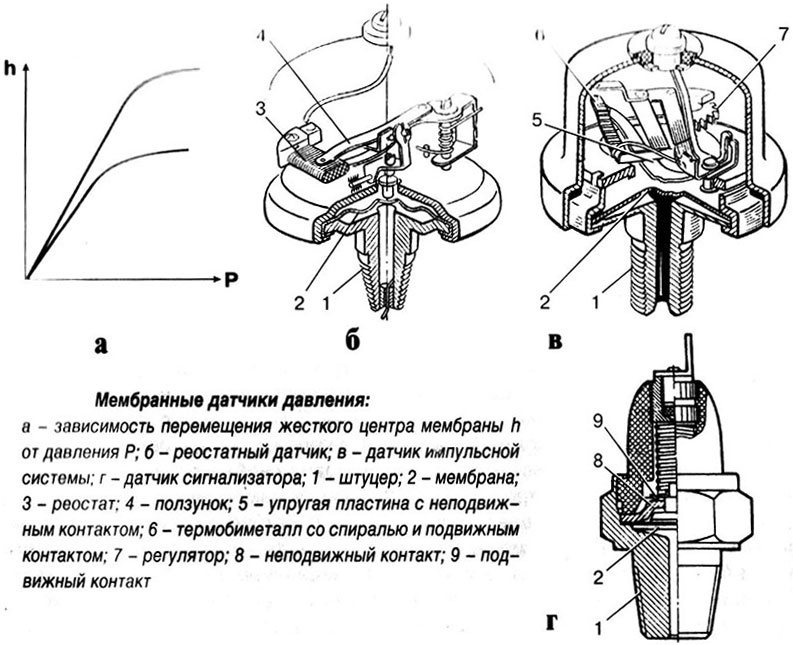
The main types of diaphragm (diaphragm) oil pressure sensors
Today, oil pressure sensors use transmission mechanisms and converters that are different in design and principle of operation, in total four types of devices can be distinguished:
• The contact-type sensor is only the sensors of the signaling device ("on the lamp");
• Rheostat sensor;
• Pulse sensor;
• Piezocrystalline sensor.
Each of the devices has its own design features and principle of operation.

Contact oil pressure sensor (per lamp)
The sensor is of contact type. The device has a contact group - a movable contact located on the membrane, and a fixed contact connected to the device body. The position of the contacts is selected in such a way that at normal oil pressure in the system the contacts are open, and at low pressure they are closed. The threshold pressure is set by a spring, it depends on the type and model of the engine, so contact type sensors are not always interchangeable.
Rheostat sensor. The device has a fixed wire rheostat and a slider connected to the membrane. When the membrane deviates from the average position, the slider rotates around the axis by means of a rocking chair and slides along the rheostat - this leads to a change in the resistance of the rheostat, which is monitored by a measuring device or electronic unit. Thus, the change in oil pressure is reflected in the change in the resistance of the sensor, which is used for measurements.
Pulse sensor. The device has a thermobimetallic vibrator (transducer) that has a rigid connection with the membrane. The vibrator consists of two contacts, one of which (the upper one) is made of a bimetallic plate with a heating coil wound on it. In the cold state, the bimetallic plate is straightened and closed with the bottom contact - current flows through the closed circuit, including the heating coil. Over time, the spiral heats the bimetallic plate, it bends and moves away from the lower contact - the circuit opens. Due to the break in the circuit, the spiral stops heating, the bimetallic plate cools down and straightens - the circuit closes again and the process begins again. As a result, the bimetallic plate constantly vibrates and an alternating current of a particular frequency is formed at the output of the sensor.
The lower contact of the sensor is connected to the diaphragm, which, depending on the oil pressure, deviates from the middle position up or down. In the case of lifting the diaphragm (with an increase in oil pressure), the lower contact rises and is pressed harder against the bimetallic plate, so the vibration frequency decreases, the contacts are in a closed position for a longer time. When the membrane is lowered, the lower contact moves away from the bimetallic plate, so the vibration frequency increases, the contacts are in a closed position for less time. Changing the duration of the contacts in a closed state (that is, changing the frequency of the alternating current at the output of the sensor) and is used by an analog device or electronic unit to measure the oil pressure in the engine.
Piezocrystalline sensor. This sensor has a piezocrystalline transducer connected to the membrane. The basis of the transducer is a piezocrystalline resistor - a crystal with piezoelectric properties, to the two planes of which direct current is supplied, and the perpendicular planes are connected to the membrane and a fixed base plate. When the oil pressure changes, the membrane deviates from its average position, which leads to a change in pressure on the piezocrystalline resistor - as a result, the conductive properties of the resistor and, accordingly, its resistance change. The change in current at the output of the sensor is used by the control unit or indicator to measure the oil pressure in the engine.
All sensors, regardless of type, have a cylindrical metal case, a threaded fitting is provided on the bottom of the housing for connection to the oil line (sealing washers are used for sealing), and a contact for connection to the electrical system is located on the top or side. The second contact is the housing, through the engine block connected to the ground of the electrical system. There is also a hexagon on the body for mounting and dismantling the sensor using a conventional wrench.
Issues of selection and replacement of oil pressure sensors
Oil pressure sensors (alarms and pressure measurements) are important for monitoring the operation of the engine, so if they fail, they must be changed - as a rule, they cannot be repaired. The need to replace the sensor may be indicated by incorrect readings of the device or the constant operation of the indicator on the dashboard. If the oil level in the system is normal, and there are no problems with the engine, then you need to replace the sensor.
For replacement, it is necessary to select sensors only of those types and models that are recommended by the engine manufacturer. The use of a different sensor model may lead to a violation of the readings of the measuring instrument or indicator on the dashboard. This is especially true for alarm sensors - they are usually not adjustable and are set to a certain threshold pressure at the factory. With oil pressure sensors, the situation is different - in many cases it is possible to use other types and models of devices, since the measuring device or electronic control unit offers the ability to adjust (calibrate) to a new sensor.
Replacing the oil pressure sensor is quite simple. Work should be carried out only on a stopped and cold engine, since in this case there is no oil in the main oil line (or there is very little of it), and there will be no leakage when the sensor is dismantled. The sensor simply needs to be unscrewed with a key, and a new device should be screwed in its place. A sealing washer must be put on the sensor fitting, otherwise the system may lose its tightness.
With the correct selection and replacement of the sensor, the critical oil pressure drop alarm system and the engine oil pressure measurement system will work reliably, providing the necessary monitoring of the condition of the power unit.
Post time: Aug-18-2023
