
The pneumatic system of cars and tractors operates normally in a certain pressure range, when the pressure changes, its failures and breakdowns are possible. The constancy of the pressure in the system is provided by the regulator - read about this unit, its types, structure, operation, as well as repairs and adjustments in the article.
What is a pressure regulator?
Pressure regulator is a component of the pneumatic system of vehicles and various equipment; A device that ensures the constancy of air pressure in the system, and performs several protective and preventive functions.
This unit solves the following tasks:
• Maintaining the air pressure in the system in a predetermined range (650-800 kPa, depending on the type of equipment);
• Protection of the pneumatic system from pressure increase above the established limit (above 1000-1350 kPa, depending on the type of equipment);
• Prevention and protection of the system from contamination and corrosion due to the periodic discharge of condensate into the atmosphere.
The main function of the regulator is to maintain the air pressure in the system within the established operating range, regardless of the current loads, the number of connected consumers, climatic conditions, etc. Finally, during the normal pressure relief through the regulator, the condensate accumulated in the components of the system (mainly in a special condensing receiver) is removed into the atmosphere, which protects them from corrosion, freezing and contamination.
The device and principle of operation of the pressure regulator
There are many types and models of pressure regulators on the market today, but they all fall into two large groups:
• Standard regulators;
• Regulators combined with an adsorber.
Devices of the first type regulate the pressure in the system and perform protective functions, while air dehumidification is carried out by a separate component - a moisture and oil separator (or a separate oil separator and air dryer). Devices of the second type are equipped with an adsorber cartridge, which provides additional air dehumidification, providing better protection for the pneumatic system.
All regulators have a fundamentally identical device, each of them provides several basic elements:
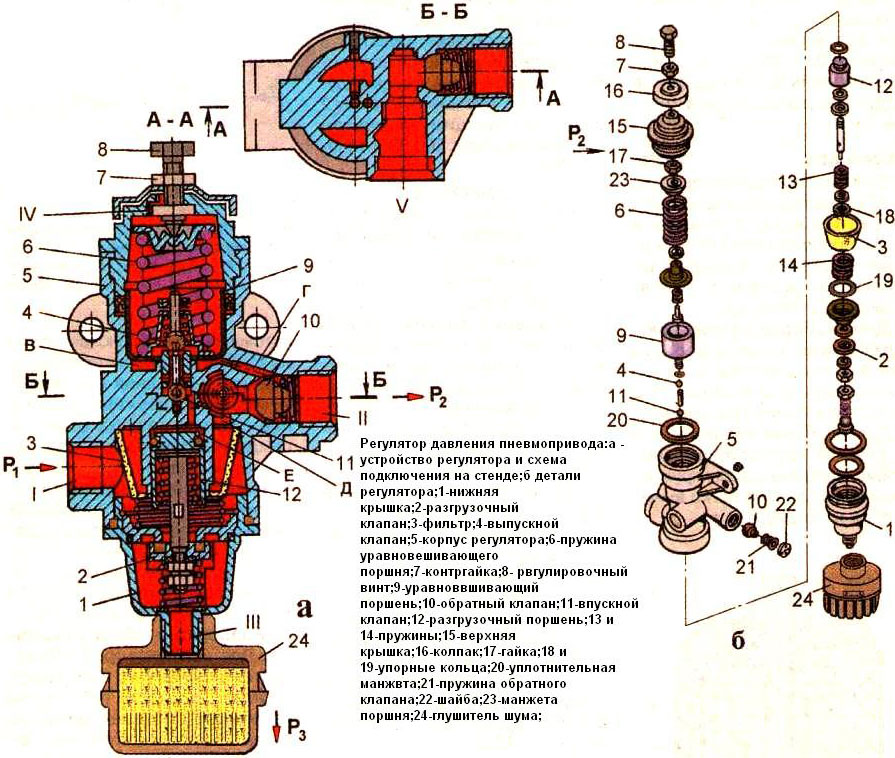
Pressure regulator design
• Intake and exhaust valves on the same stem;
• Non-return valve (located on the side of the outlet pipe, it prevents the pressure drop in the system when the compressor is turned off);
• Discharge valve (located on the side of the lower atmospheric outlet, provides air discharge into the atmosphere);
• Balancing piston connected to the intake and exhaust valves (provides opening / closing of the intake and exhaust valves, redirects air flows inside the regulator).
All parts and components of the unit are located in a metal case with a system of channels and cavities. The regulator has four outlets (pipe) for connection to the pneumatic system of the car: inlet - compressed air from the compressor enters it, output - through it the air from the regulator enters the system, atmospheric - compressed air and condensate are discharged into the atmosphere through it, and special for inflating tires. The atmospheric outlet can be equipped with a muffler - a device to reduce the intensity of noise arising from pressure relief. The tire inflation outlet is made in the form of a hose connection, it is closed with a protective cap. Also, the regulator provides another atmospheric output of small cross-section, it is necessary for the normal operation of the discharge piston, pipelines are not connected to this terminal.
In regulators with an adsorber, a container filled with hygroscopic material is attached to the housing, absorbing moisture from the air coming from the compressor. Usually, the adsorber is made in the form of a standard cartridge with a threaded mount, which can be replaced if necessary.
The operation of the pressure regulator is not too complicated. When the engine starts, compressed air from the compressor enters the corresponding terminal of the regulator. As long as the pressure is in the operating range or less, the valves are in a position in which air flows freely through the regulator into the system, fills the receivers and ensures the operation of consumers (the exhaust and check valves are open, the intake and discharge valves are closed). When the pressure approaches the upper limit of the operating range (750-800 kPa), the unloading and inlet valves open, and the check and exhaust valves close, as a result, the air path changes - it enters the atmospheric outlet and is discharged. Thus, the compressor begins to idle, the increase in pressure in the system stops. But as soon as the pressure in the system drops to the lower limit of the operating range (620-650 kPa), the valves move to a position at which the air from the compressor begins to flow back into the system.
In the event that the regulator turns off the compressor when the pressure reaches 750-800 kPa, then in the future the safety mechanism will work, the role of which is played by the same discharge valve. And if the pressure reaches 1000-1350 kPa, then the unloading valve opens, but the remaining components of the unit do not change their position - as a result, the system is connected to the atmosphere, an emergency pressure release occurs. When the pressure drops, the discharge valve closes and the system continues to operate normally.
The pressure at which the compressor is disconnected from the pneumatic system is set by the force of the spring of the balancing piston. It can be changed by means of an adjusting screw resting on the spring plate. The screw is fixed by a locknut, which prevents the mechanism from being deadjusted due to vibrations, shocks, jolts, etc.
Regulators with an adsorber work similarly, but they provide two additional functions. First, when the pressure is released, the air is not just released into the atmosphere - it passes through the adsorber in the opposite direction, removing accumulated moisture from it. And, secondly, when the adsorber is clogged (the air from the compressor is filtered, but there is always a certain amount of contaminants in it, which are deposited on the adsorbent particles), the bypass valve is triggered, and the air from the discharge line enters directly into the system. In this case, the air is not dehumidified, and the adsorber must be replaced.
A pressure regulator of any type is installed in the discharge line of the pneumatic system immediately behind the compressor and the oil and moisture separator (if it is provided in the system). The air from the regulator, depending on the circuit of the pneumatic system, can be supplied to the freeze fuse and then to the safety valve, or first to the condensing receiver and then to the safety valve. In this way, the regulator monitors the pressure in the entire system and protects it from overloads.
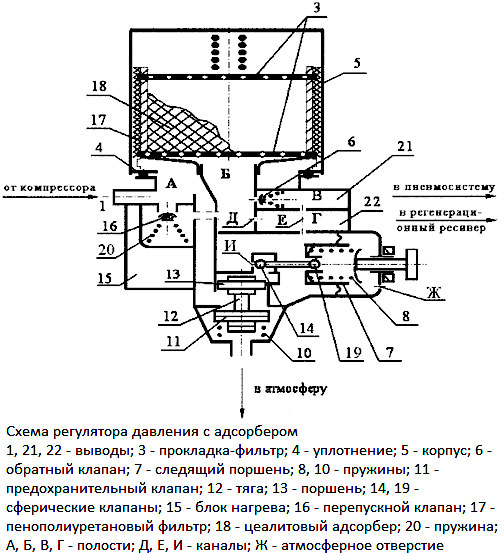
Diagram of a pressure regulator with an adsorber
Issues of selection and repair of pressure regulators
During operation, the pressure regulator is exposed to contamination and serious loads, which gradually leads to a deterioration in its efficiency and breakdowns. The extension of the service life of the regulator is achieved by its inspection and cleaning during seasonal maintenance of the vehicle. In particular, it is necessary to clean the strainers built into the regulators and check the entire unit for leaks. In regulators with an adsorber, it is also necessary to replace the cartridge with the adsorbent.
In case of malfunctions of the regulator - leaks, incorrect operation (failure to turn off the compressor, delay in air discharge, etc.) - the unit must be repaired or replaced in the assembly. In case of replacement, you should choose a regulator of the same type and model that is installed on the car (or its analogue corresponding to the characteristics of the pneumatic system). After installation, the new device must be adjusted in accordance with the recommendations of the vehicle manufacturer. With the right choice and replacement of the regulator, the pneumatic system will work reliably in a wide variety of conditions.
Post time: Aug-05-2023
