
All modern vehicles are equipped with an audible signal, which is used to prevent traffic accidents. Read about what a sound signal is, what types it is, how it works and what its work is based on, as well as the choice of signals and their replacement.
What is a beep?
Sound signal (sound signaling device, ZSP) - the main element of the sound alarm of vehicles; An electrical, electronic or pneumatic device that emits an audible signal of a certain tone (frequency) to warn other road users in order to prevent dangerous situations.
In accordance with the current Rules of the Road, every vehicle operated in Russia must be equipped with an audible warning device, which should be used only to prevent traffic accidents. In accordance with paragraph 7.2 of the "List of malfunctions and conditions under which the operation of the vehicle is prohibited", the breakdown of the sound signal is the reason for the prohibition of the operation of the car. Therefore, a faulty ZSP must be replaced, and in order to make the right choice of this device, you should understand its types, parameters and key features.
Types, structure and principle of operation of sound signals
The ZSP on the market can be divided into several types according to the principle of operation, spectral composition and tone of the emitted sound.
According to the principle of operation laid down in them, all devices are divided into three main groups:
● Electric;
● Pneumatic and electro-pneumatic;
● Electronic.
The first group includes all ZSP, in which the sound is generated by a membrane, oscillating under the action of alternating current in a solenoid (electromagnet). The second group includes signals in which the sound is formed by the flow of air passing through the horn from a car or its own compressor, these devices are usually called horns. The third group includes a variety of devices with electronic sound generators.
According to the spectral composition of the emitted sound, there are two types of ZSP:
● Noise;
● Tonal.
The first group includes signals that emit sound of a wide range of frequencies (from tens to thousands of Hz), perceived by our ear as a sharp jerky sound or just noise. The second group includes ZSP that emit sound of a certain height in the range of 220-550 Hz.
At the same time, tonal ZSP can operate in two ranges:
The design of the membrane (disk) sound signal The design of the pneumatic sound signal
● Low tone - in the range of 220-400 Hz;
● High tone - in the range of 400-550 Hz.
It should be noted that these frequencies correspond to the basic tone of the sound signal, but each such device emits sound and other frequencies up to a dozen kilohertz.
Each of the types of ZSP has its own characteristics and applications, they should be considered in more detail.
Membrane (disk) sound signals
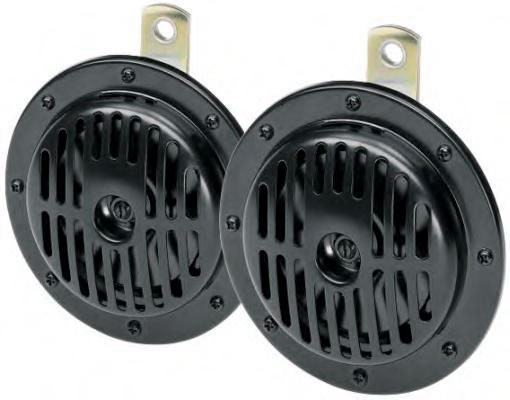

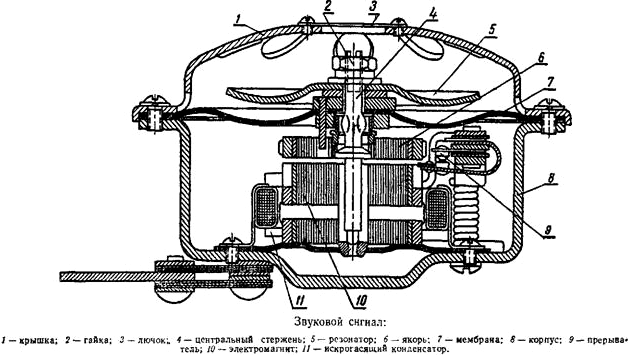
Membrane (disk) sound signals
Devices of this design are called electromagnetic, electromechanical or vibration. Structurally, the signal is simple: it is based on an electromagnet with a movable armature connected to a metal membrane (or disk) and in contact with the contact group. This whole structure is placed in a case, covered with a membrane on top, a resonator can be additionally installed on the membrane - a flat or cup-shaped plate to increase the volume of sound. The body has a bracket and terminals for connecting to the car's electrical system.
The principle of operation of the disk ZSP is simple. At the moment of applying current to the electromagnet, its armature is retracted and rests against the contacts, opening them - the electromagnet is de-energized and the armature returns to its original position under the action of the spring or the elasticity of the membrane, which again leads to the closure of the contacts and the supply of current to the electromagnet. This process is repeated at a frequency of 200-500 Hz, the vibrating membrane emits sound of the appropriate frequency, which can additionally be amplified by the resonator.
Vibration electromagnetic signals are the most common due to their simple design, low cost and durability. They are presented on the market in a wide variety, there are options for low and high tones, which are often put on the car in pairs.
Membrane horn ZSP
Devices of this type are similar in design to the signals discussed above, but have an additional detail - a straight horn ("horn"), spiral ("cochlea") or another type. The back of the horn is located on the side of the membrane, so the vibration of the membrane causes all the air located in the horn to vibrate - this provides sound emission of a certain spectral composition, the tone of the sound depends on the length and internal volume of the horn.
The most common are compact "snail" signals, which take up little space and have high power. Slightly less common are the "horn" signals, which, when enlarged, have an attractive appearance and can be used to decorate a car. Regardless of the type of horn, these ZSPs have all the advantages of conventional vibration signals, which ensured their popularity.
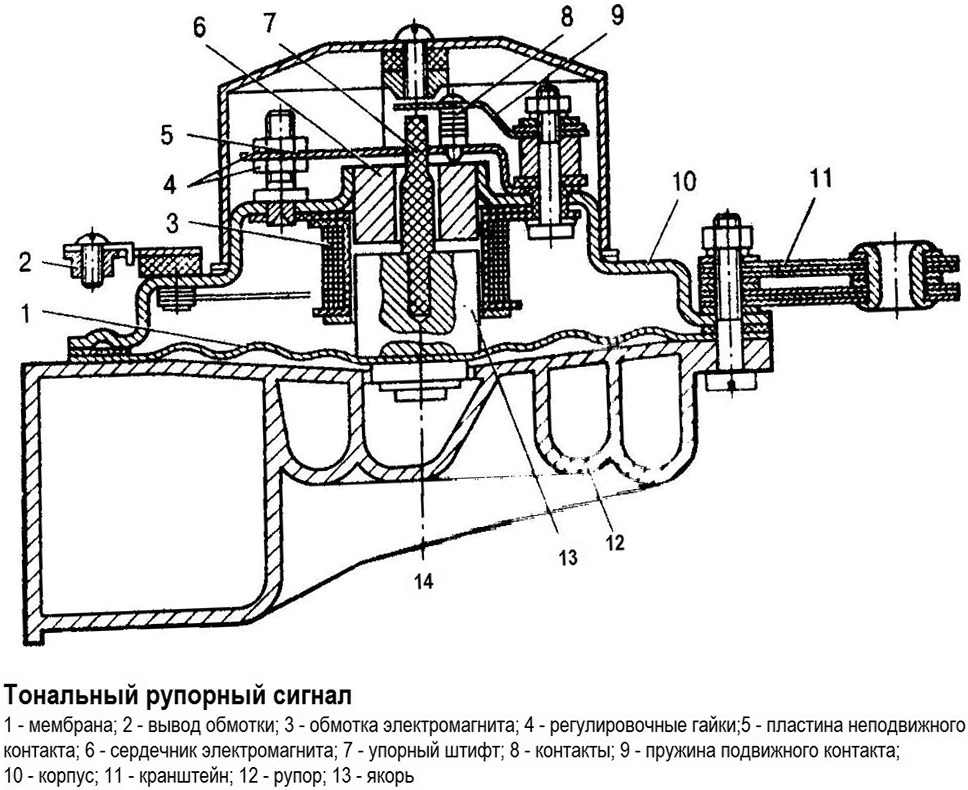
The design of the horn membrane sound signal
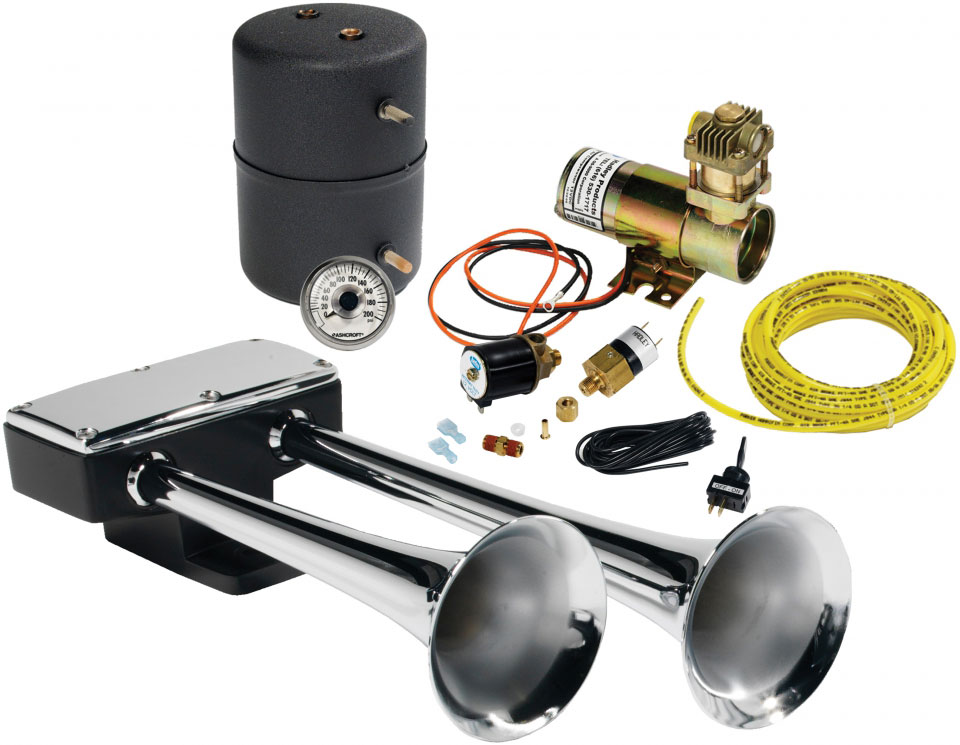
Pneumatic and electro-pneumatic sound signals

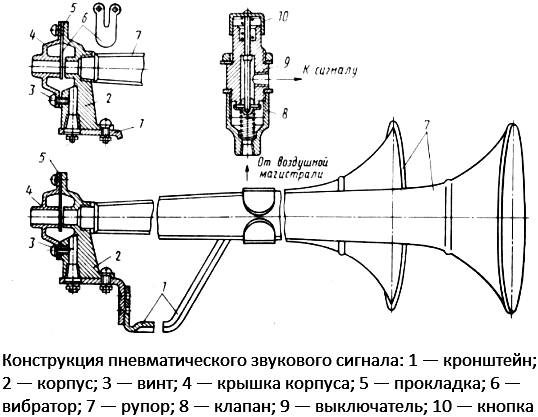
Electro-pneumatic horn
ZSP of this type is based on the simple principle of sound production from a thin plate oscillating in the air stream. Structurally, the pneumatic signal is a straight horn, on the narrow part of which there is a closed air chamber with a reed or membrane vibrator - a small cavity inside which there is a plate of one shape or another. High-pressure air (up to 10 atmospheres) is supplied to the chamber, it causes the plate to vibrate - this part emits a sound of a particular frequency, which is amplified by the horn.
There are two variants of signals - pneumatic, requiring connection to the pneumatic system of the car, and electropneumatic, having their own compressor with an electric drive. Regardless of the type, two or three or more ZSPs with different tones are installed on the vehicle, which achieves the desired frequency and intensity of sound.
Today, pneumatic signals are the least common due to their high cost, but they are indispensable for high-noise trucks, these devices are also used for tuning.
Electronic ZSP
Devices of this type are based on electronic generators of sound frequency, the emission of sound in which is carried out by dynamic heads or electric emitters of other types. The advantage of this signal is the ability to emit any sound signal, but such devices are more expensive and less reliable than conventional membrane or pneumatic ones.
GOSTs and legal issues of operation of sound signals
The main parameters of sound-emitting devices are standardized, and the scope of their application is strictly regulated. All ZSPs must comply with GOST R 41.28-99 (which, in turn, meets the European UNECE Regulation No. 28). One of the main characteristics of ZSP is the sound pressure they develop. This parameter should be in the range of 95-115 dB for motorcycles, and in the range of 105-118 dB for cars and trucks. In this case, the sound pressure is measured in the frequency range of 1800-3550 Hz (that is, not on the fundamental tone of the ZSP radiation, but in the area to which the human ear is most sensitive).
It is specifically stipulated that civilian vehicles must be equipped with signals that have a sound frequency that is constant over time. This means that not only a variety of musical ZSPs are prohibited on ordinary cars, but also special signals such as sirens, "quacks" and others. Special-purpose signals are used only on certain categories of vehicles specified in the standard GOST R 50574-2002 and others. Unauthorized use of such signals leads to administrative liability.
Issues of selection and installation of the sound signal
The selection of the ZSP to replace the faulty one should be done based on the type of previously installed signal and its characteristics. It is best to use a device of the same type and model (and hence the catalog number) that was used on the vehicle earlier. However, it is quite permissible to install analogues (but not on a warranty car) that meet the requirements for sound pressure and spectral composition. Also, the new signal must have the necessary electrical characteristics (12 or 24 V power supply) and type, mounts and terminals.
It is unacceptable to use devices with a variable frequency of sound, and if two devices of different frequencies are installed on the car, then you can not put both high or low tone signals. It also makes no sense to use a high-intensity pneumatic signal on passenger cars - this can lead to certain problems with the law.
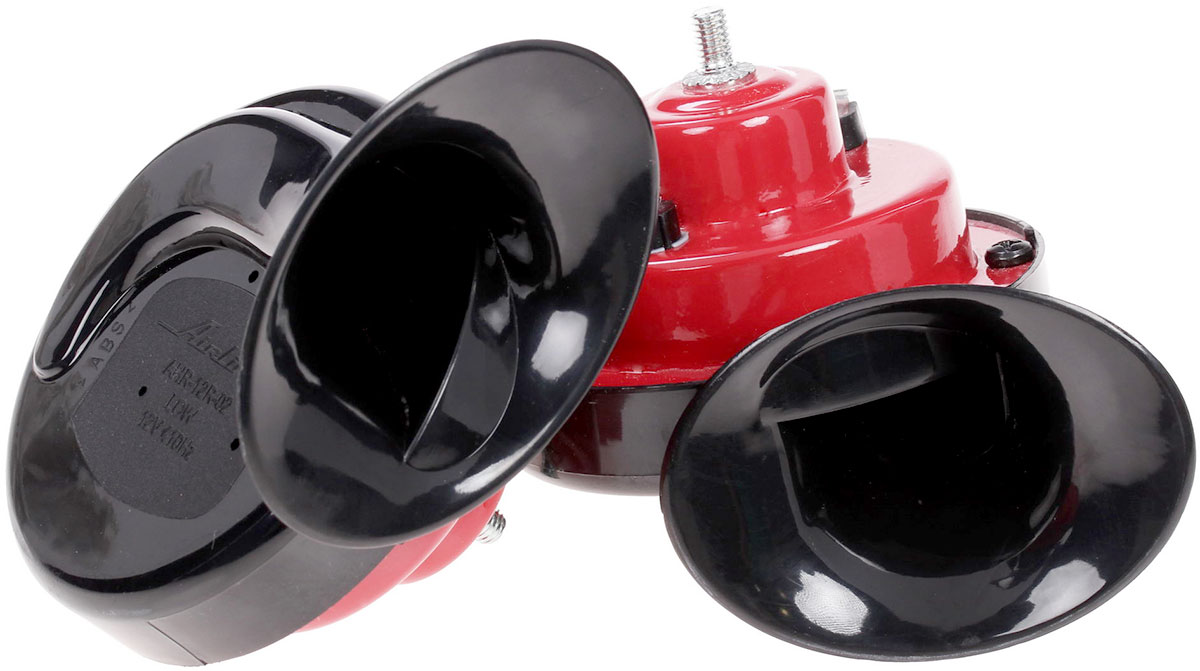

Horn electromagnetic sound signals
Replacement of the ZSP must be carried out in accordance with the instructions for repair and maintenance of the vehicle, and the installation of an abnormal signal - according to the instructions attached to it. Usually, this work comes down to unscrewing one or two screws and connecting electrical connectors.
With the correct selection and replacement of the sound signal, the car will meet safety requirements and can be operated normally in any conditions.
Post time: Jul-26-2023
