
The normal operation of the starter is provided by a special mechanism - the starter drive (popularly nicknamed "Bendix"), which combines an overrunning clutch, a gear and a drive fork. Read about what a starter drive is, what types it is, how it is designed and works in this article.
What is a starter drive?
The starter drive is the mechanism of the internal combustion engine starting system, which is the link between the electric starter and the engine flywheel. The actuator has two functions:
• Connecting the starter to the engine to transfer torque from the starter motor to the crankshaft flywheel;
• Protection of the starter from overload after starting the engine.
The protective function of the starter drive is of key importance. To start the power unit, it is necessary that its crankshaft rotates at a frequency of 60-200 rpm (for gasoline - less, for diesel engines - more) - it is for this angular velocity that the starter is designed. However, after starting, the rpm increases to 700-900 or more, in which case the torque changes directions, coming from the flywheel to the starter. The increased speed is dangerous for the starter, so if the engine is successfully started, its flywheel must be disconnected from the starter - this is the function that the drive solves.
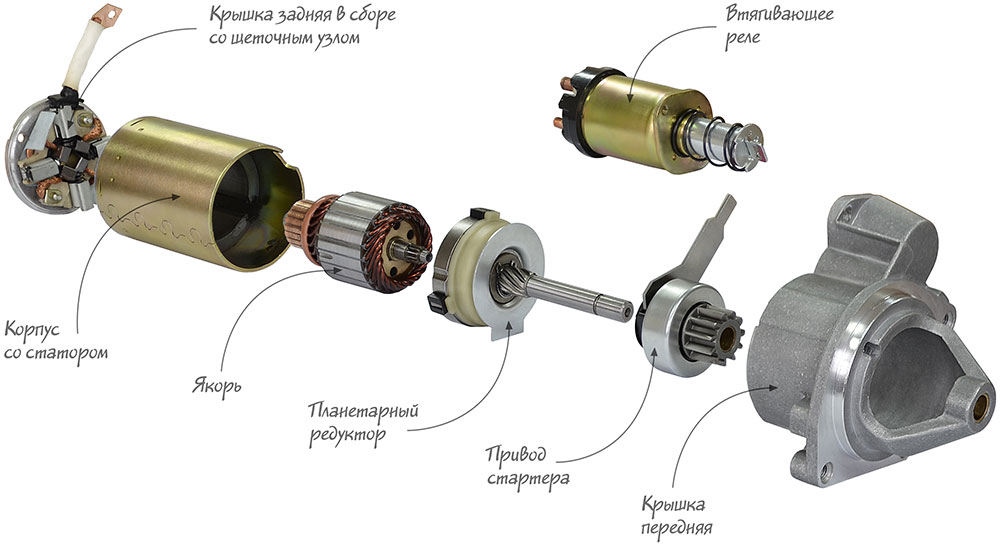
Structurally, the starter drive combines three mechanisms:
• Flywheel drive gear;
• Overrunning clutch (or freewheel);
• Drive lever or fork with leash, sleeve or actuator clutch.
Each of the mechanisms has its own functions. The drive lever connected to the starter traction relay brings the drive to the flywheel of the motor, ensuring that the gear engages with the ring. The drive gear transmits torque from the starter to the flywheel ring. And the overrunning clutch ensures the transmission of torque from the starter rotor to the gear at the moment the engine starts, and separates the drive and flywheel after a successful engine start.
It is interesting to note that the starter drive was popularly called "Bendix" - this is due to the French company Bendix. In the past, spare parts of this brand gained fame in our country, and over time the name became a household name. Today, every motorist, having heard the word "Bendix", understands that we are talking about the starter drive.
Types of starter drives
The starter drives used today are divided into types according to the design of the overrunning clutch and the method of attaching the drive lever (fork).
The lever can be connected to the actuator in three ways:
• Using a coupling with an annular chute - the protrusions on the fork horns are located in the chute;
• Using a leash with two grooves for the protrusions on the fork horns;
• Using a leash with two pins (rectangular, cylindrical), on which the fork horns with holes of the appropriate shape are put on.
At the same time, starter drives can be sold both with and without a lever.
According to the design of the overrunning clutch, starter drives are divided into two large groups:
• With roller overrunning clutch;
• With ratchet overrunning clutch.
Today, roller couplings are most used, which have a simpler design, reliability and high resistance to negative environmental influences and engine compartment (water, oils, dirt, temperature extremes, etc.). Starter drives with a ratchet overrunning clutch are more often installed on trucks with powerful power units. Ratchet couplings can operate under high loads and at the same time have small weight and size indicators, and most importantly, they provide a more complete interruption of torque.
The design and principle of operation of the starter drive with a roller overrunning clutch
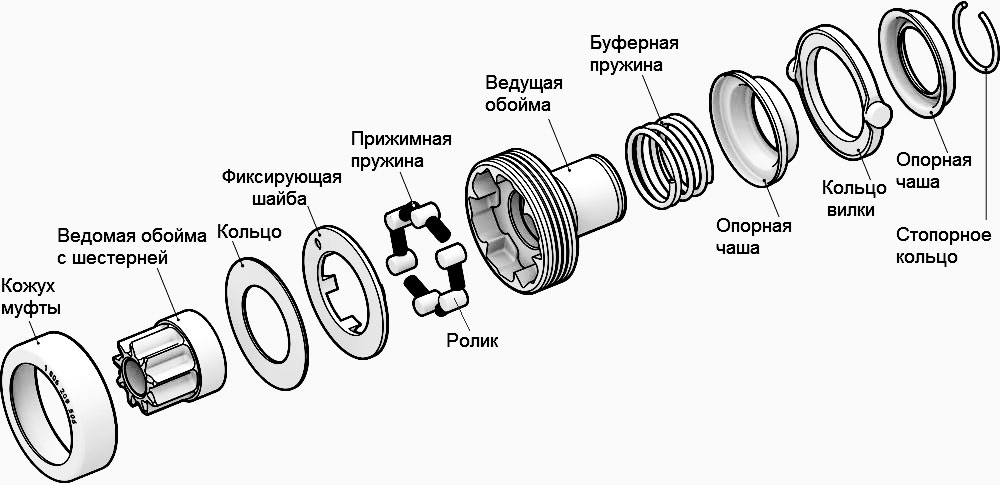
The basis of the design of the starter drive with a freewheel roller clutch is the drive (outer) cage, in the expanded part of which cavities of variable cross-section are carved for the installation of rollers and their pressure springs. Inside the drive cage, a driven cage is installed, combined with the drive gear, which, during the operation of the starter, engages with the flywheel crown. Rollers are installed in the space between the outer surface of the driven cage and the cavities of the drive cage, they move into the narrow part of the cavities with the help of springs (and sometimes additional plungers). The loss of the rollers is prevented by a locking washer, and the whole structure is assembled together by the coupling casing.
On the shank of the drive clip there is a coupling, leash or fork attachment ring, it is planted freely, and rests against the expanded part of the clip through a damping spring. To prevent the fork clutch from sliding off the shank of the clip, it is fixed with a retaining ring. The inner part of the drive clip has splines that engage with the splines on the rotor shaft of the starter or gearbox. By means of a spline connection, the torque from the shaft is transmitted to the drive cage and the entire starter drive.
The drive with a roller overrunning clutch functions as follows. When the ignition is turned on, the starter traction relay is triggered, its armature pulls the fork, which, in turn, pushes the drive towards the flywheel. In order for the drive gear to engage the flywheel, its teeth have bevels, and a damping spring also helps here (it also reduces the force of the mechanism's impacts, preventing damage to the teeth and other parts). At the same time, the starter motor starts, and the torque from its shaft is transmitted to the drive cage. Under the action of springs, the rollers in the cage are located in the narrowest part of the cavities, due to which there are large frictional forces between the walls of the cavities, the rollers and the outer surface of the driven cage. These forces ensure the rotation of the drive and driven clips, as a whole - as a result, the torque from the starter is transmitted to the flywheel crown, and the engine crankshaft rotates.

With the successful start of the power unit, the angular velocity of the flywheel increases, and the torque from it begins to be transmitted to the starter. When a certain angular velocity is reached, the rollers move through the cavities under the action of centrifugal forces, passing into the expanded part. As a result of this movement, the frictional forces between the drive and driven clips decrease, and at some point the parts are separated - the torque flow is interrupted, and the starter rotor stops rotating. At the same time, the starter is turned off, and the drive under the action of the spring (as well as oblique teeth on the shaft) is removed from the flywheel, returning to its original position.
Today, there are many variations in the design of the roller overrunning clutch, but they all have the principle of operation described above. The starter drive with a roller clutch is easily recognizable by its appearance - the clutch has the shape of a ring of small width on the side of the gear.
The design and principle of operation of the starter drive with a ratchet overrunning clutch
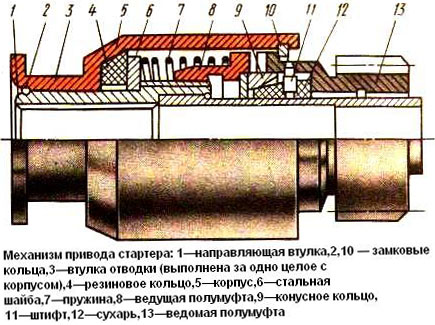
The basis of the design of the ratchet freewheel clutch is a pair formed by the drive and driven by half-couplings, at the ends of which sawtooth teeth are made. The drive half coupling is located on the guide sleeve, having a connection to it by means of a tape thread, and inside the sleeve there are straight splines for connection with the starter shaft. On the opposite side, also on the bushing, but only without a rigid connection, there is a driven half coupling, made together with the drive gear. Sawtooth teeth are also made at the end of the driven clutch, which can engage with the teeth of the drive half coupling.
Under the coupling halves there is a locking mechanism consisting of a ring with a conical groove connected to the drive half coupling, and crackers having a pin connection with the driven half coupling. In the non-working position, the ring presses the breadcrumbs against the sleeve. From above, the coupling halves are closed with a body in the form of an open glass, on its open side there is a lock ring that prevents the driven coupling half from sliding off the sleeve.
The drive with a ratchet overrunning clutch works as follows. When the ignition is turned on, as in the previous case, the drive is brought to the flywheel, and the gear engages with the crown. In this case, an axial force occurs, due to which both coupling halves engage - rotation from the starter is transmitted to the gear and flywheel. When the engine starts, the torque flow changes direction, the driven clutch half begins to rotate faster than the leading one. However, during the reverse rotation, engagement between the teeth of the clutch is no longer possible - due to the presence of bevels, the teeth slide over each other, and the drive half coupling moves away from the driven one. At the same time, the ring with a conical groove that presses the breadcrumbs of the locking mechanism is pushed back, and the crackers rise along the pins under the action of centrifugal forces. Having reached the top point, the crackers are pressed against the ring, fixing the coupling halves at some distance from each other - as a result, the flow of torque is interrupted. After the starter is turned off, the driven clutch half stops rotating, the crackers slide down, removing the lock, and the drive returns to its original position.
The starter drive with a ratchet overrunning clutch is easily recognizable by its appearance - it has the shape of a glass, inside of which the coupling halves are located. Such mechanisms are now used on trucks MAZ, Ural, KamAZ and some others.
Post time: Aug-22-2023
