
Every car has a simple but important sensor that helps monitor engine performance - a coolant temperature sensor. Read about what a temperature sensor is, what design it has, on what principles its work is based, and what place it occupies in the car.
What is a temperature sensor
Coolant temperature sensor (DTOZh) is an electronic sensor designed to measure the temperature of the coolant (coolant) of the cooling system of an internal combustion engine. The data obtained by the sensor is used to solve several problems:
• Visual control of the temperature of the power unit - data from the sensor is displayed on the corresponding device (thermometer) on the dashboard in the car;
• Adjustment of the operation of various engine systems (power, ignition, cooling, exhaust gas recirculation and others) in accordance with its current temperature regime - information from the DTOZH is fed to the electronic control unit (ECU), which makes appropriate adjustments.
Coolant temperature sensors are used in all modern cars, they have fundamentally the same design and principle of operation.
Types and design of temperature sensors
In modern vehicles (as well as in various electronic devices), temperature sensors are used, the sensitive element in which is a thermistor (or thermistor). A thermistor is a semiconductor device whose electrical resistance depends on its temperature. There are thermistors with a negative and positive temperature coefficient of resistance (TCS), for devices with a negative TCS, the resistance decreases with increasing temperature, for devices with a positive TCS, on the contrary, it increases. Today, thermistors with negative TCS are most often used, as they are more convenient and cheaper.
Structurally, all automobile DTOZh are fundamentally the same. The basis of the design is a metal body (cylinder) made of brass, bronze or other corrosion-resistant metal. The body is made in such a way that its part is in contact with the coolant flow - here is a thermistor, which can additionally be pressed by a spring (for more reliable contact with the case). In the upper part of the body there is a contact (or contacts) for connecting the sensor to the corresponding circuit of the vehicle's electrical system. The case is also threaded and a turnkey hexagon is made for mounting the sensor in the engine cooling system.
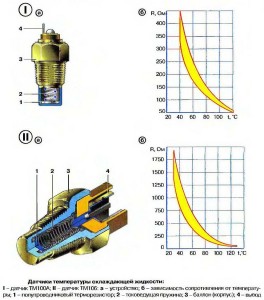
Temperature sensors differ in the way they are connected to the ECU:
• With a standard electrical connector — the sensor has a plastic connector (or block) with contacts;
• With screw contact — one contact with a clamping screw is made on the sensor;
• With pin contact - one pin or spatula contact is provided on the sensor.
Sensors of the second and third types have only one contact, the second contact is the sensor body, connected to the "ground" of the car's electrical system through the engine. Such sensors are most often used on commercial vehicles and trucks, on special, agricultural and other equipment.
The coolant temperature sensor is mounted at the hottest point of the engine cooling system - in the exhaust pipe of the cylinder head. On modern cars, two or even three DTOZhS are often installed at once, each of which performs its function:
• The thermometer sensor (coolant temperature indicator) is the simplest, has low accuracy, since it only helps to visually assess the temperature of the power unit;
• The ECU sensor at the outlet of the head of the unit is the most responsible and accurate sensor (with an error of 1-2.5 ° C), which allows you to track temperature changes of several degrees;
• Radiator outlet sensor - an auxiliary sensor of low accuracy, which ensures timely switching on and off of the electric radiator cooling fan.
Several sensors provide more information about the current temperature regime of the power unit and allow you to more reliably monitor its operation.
The principle of operation and the place of the temperature sensor in the vehicle
In general, the principle of operation of the temperature sensor is simple. A constant voltage (usually 5 or 9 V) is applied to the sensor, and the voltage drops on the thermistor in accordance with Ohm's law (due to its resistance). A change in temperature entails a change in the resistance of the thermistor (when the temperature rises, the resistance decreases, when the temperature decreases, it increases), and hence the voltage drop in the sensor circuit. The measured value of the voltage drop (or rather, the actual voltage in the sensor circuit) is used by a thermometer or ECU to determine the current temperature of the engine.
For visual control of the temperature of the power unit, a special electrical device is connected to the sensor circuit - a ratiometric thermometer. The device uses two or three electrical windings, between which there is a movable armature with an arrow. One or two windings produce a constant magnetic field, and one winding is included in the temperature sensor circuit, so its magnetic field changes depending on the coolant temperature. As a result of the interaction of constant and alternating magnetic fields in the windings, it causes the armature to rotate around its axis, which entails a change in the position of the thermometer needle on its dial.

To control the functioning of the motor in various modes and control its systems, the sensor readings are fed to the electronic control unit through the appropriate controller. The temperature is measured by the magnitude of the voltage drop in the sensor circuit, for this purpose in the ECU memory there are tables of correspondence between the voltage in the sensor circuit and the engine temperature. Based on these data, various algorithms for the operation of the main engine systems are launched in the ECU.
Based on the readings of the DTOZH, the operation of the ignition system is adjusted (changing the ignition timing), power supply (changing the composition of the fuel-air mixture, its depletion or enrichment, throttle assembly control), exhaust gas recirculation and others. Also, the ECU, in accordance with the engine temperature, sets the crankshaft speed and other characteristics.
The temperature sensor on the cooling radiator works in a similar way, it is used to control the electric fan. On some vehicles, this sensor can be paired with the main one for more precise control of various engine systems.
The temperature sensor plays an important role in any vehicle with an internal combustion engine, in the event of a breakdown, it must be replaced as soon as possible - only in this case the normal operation of the power unit in any mode will be ensured.
Post time: Aug-24-2023
