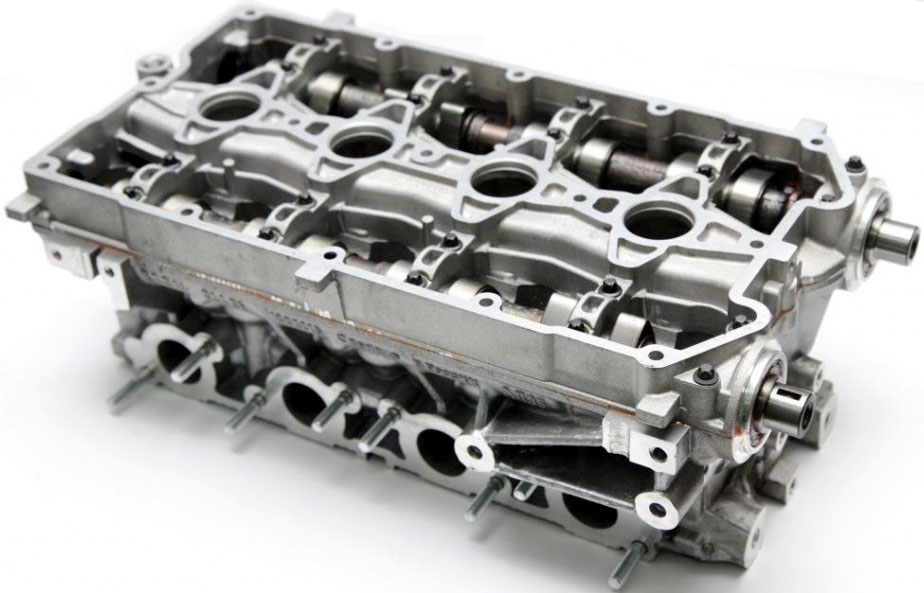

Each internal combustion engine contains a cylinder head (cylinder head) - an important part that, together with the piston head, forms a combustion chamber, and plays an important role in the operation of individual systems of the power unit. Read all about cylinder heads, their types, design, applicability, maintenance and repair in this article.
What is a cylinder head?
The cylinder head (cylinder head) is an internal combustion engine unit mounted at the top of the cylinder block.
The cylinder head is one of the main parts of the internal combustion engine, it ensures its functioning and determines its main performance characteristics. But the head is entrusted with a number of functions:
• Formation of combustion chambers - in the lower part of the head, located directly above the cylinder, a combustion chamber is performed (partially or completely), its full volume is formed when the TDC piston is reached;
• Supply of air or fuel-air mixture to the combustion chamber - the corresponding channels (intake) are made in the cylinder head;
• Removal of exhaust gases from the combustion chambers - the corresponding channels (exhaust) are made in the cylinder head;
• Cooling of the power unit - in the cylinder head there are channels of the water jacket through which the coolant circulates;
• Ensuring the operation of the gas distribution mechanism (timing) - valves are located in the head (with all related parts - bushings, seats) that open and close the intake and exhaust channels in accordance with the engine strokes. Also, the entire timing can be located on the head - the camshaft (shafts) with their bearings and gears, the valve drive, valve springs and other related parts;
• Lubrication of timing parts - channels and containers are made in the head, through which oil flows to the surfaces of rubbing parts;
• Ensuring the operation of the fuel injection system (in diesel and injection engines) and / or the ignition system (in gasoline engines) - fuel injectors and / or spark plugs with related parts (as well as diesel glow plugs) are mounted on the head;
• Acting as a body part for mounting various components - intake and exhaust manifolds, sensors, pipes, brackets, rollers, covers and others.
Due to such a wide range of functions, stringent requirements are imposed on the cylinder head, and its design can be quite complex. Also today there are many types of heads in which the described functionality is implemented in one way or another.
Types of cylinder heads
The cylinder heads differ in design, type and location of the combustion chamber, the presence and type of timing, as well as the purpose and some features.
cylinder heads can have one of four designs:
• Common head for all cylinders in in-line engines;
• Common heads for one row of cylinders in V-shaped engines;
• Separate heads for several cylinders of multi-cylinder in-line engines;
• Individual cylinder heads in single-, two- and multi-cylinder inline, V-shaped and other engines.
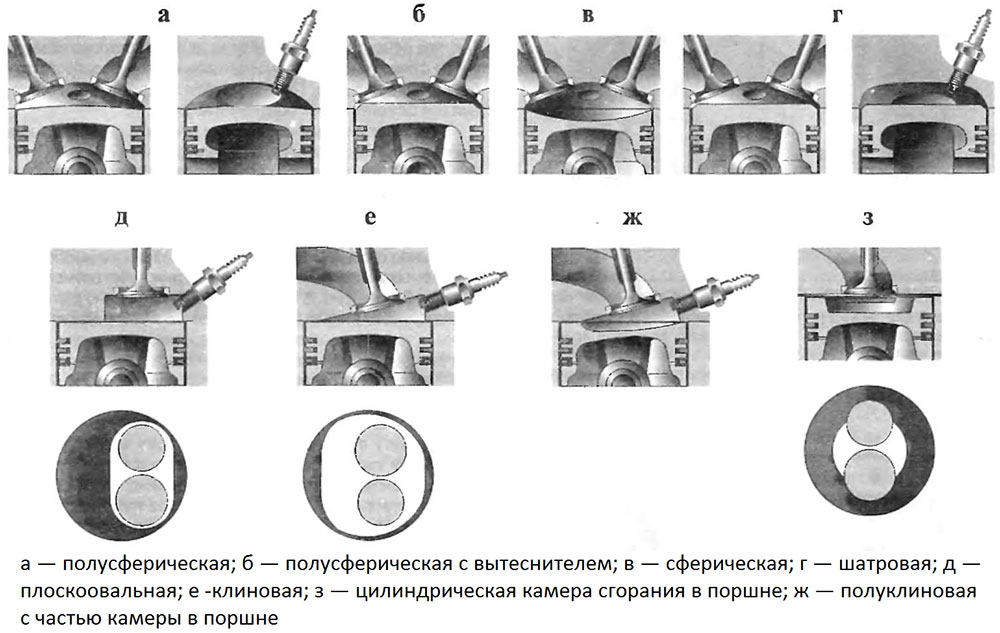
The main types of combustion chambers of internal combustion engines
In conventional 2-6-cylinder in-line engines, common heads are most often used to cover all cylinders. On V-shaped engines, both cylinder heads common to one row of cylinders and individual heads for each cylinder are used (for example, eight-cylinder KAMAZ 740 engines use separate heads for each cylinder). Separate cylinder heads of in-line engines are used much less frequently, usually one head covers 2 or 3 cylinders (for example, in six-cylinder diesel engines MMZ D-260 two heads are installed - one for 3 cylinders). Individual cylinder heads are used on powerful in-line diesel engines (for example, on Altai A-01 diesel engines), as well as on power units of a special design (boxer two-cylinder, star, etc.). And naturally, only individual heads can be used on single-cylinder engines, which also perform the functions of an air-cooled radiator.
According to the location of the combustion chamber, there are three types of heads:
• With a combustion chamber in the cylinder head - in this case, a piston with a flat bottom is used, or having a displacer;
• With a combustion chamber in the cylinder head and in the piston - in this case, part of the combustion chamber is performed in the piston head;
• With a combustion chamber in the piston - in this case, the lower surface of the cylinder head is flat (but there may be recesses for installing valves in an inclined position).
At the same time, combustion chambers can have different shapes and configurations: spherical and hemispherical, hipped, wedge and semi-wedge, flat-oval, cylindrical, complex (combined).
According to the presence of timing parts, the head of the unit are:
• Without timing - heads of multi-cylinder low-valve and single-cylinder two-stroke valveless engines;
• With valves, rocker arms and related components - engine heads with a lower camshaft, all parts are located on the top of the cylinder head;
• With full timing - camshaft, valve drive and valves with related parts, all parts are located in the upper part of the head.
Finally, the heads can be divided according to their purpose into many types - for diesel, gasoline and gas power units, for low-speed and forced engines, for water-cooled and air-cooled internal combustion engines, etc. In all these cases, cylinder heads have certain design features - dimensions, the presence of cooling or fin channels, the shape of the combustion chambers, etc. But in general, the design of all these heads is fundamentally the same.
cylinder head design

Section of the cylinder head
Structurally, the cylinder head is a solid-cast part made of a material with high thermal conductivity - today it is most often aluminum alloys, white cast iron and some other alloys are also used. All parts of the systems located in it are formed in the head - intake and exhaust channels, valve holes (valve guide bushings are pressed into them), combustion chambers, valve seats (they can be made of harder alloys), support surfaces for mounting timing parts, wells and mounting threaded holes for installing candles and / or nozzles, cooling system channels, lubrication system channels, If the head is intended for an engine with an overhead camshaft, then a bed is formed on its upper surface for laying the shaft (through the liners).
On the side surfaces of the cylinder head, filler surfaces are formed for mounting the intake and exhaust manifolds. The installation of these parts is carried out through sealing gaskets that exclude air leakage and exhaust leakage. On modern engines, the installation of these and other components on the head is carried out by means of studs and nuts.
On the lower surface of the cylinder head, a filler surface is made for mounting on the block. To ensure the tightness of the combustion chambers and channels of the cooling system, a gasket is located between the cylinder head and the business center. Sealing can be carried out by conventional gaskets made of paronite, rubber-based materials, etc., but in recent years, so-called metal packets have been increasingly used - copper-based composite gaskets with synthetic inserts.
The upper part of the head is closed with a lid (stamped metal or plastic) with an oil filler neck and a stopper. Installation of the cover is carried out through the gasket. The cover protects the timing parts, valves and springs from dirt and damage, and also prevents oil spillage while the car is moving.
Cylinder head design
Installation of the cylinder head on the block is carried out by means of studs or bolts. Studs are more preferable for aluminum blocks, as they provide a reliable clamp on the head and evenly distribute the loads in the body of the block.
The cylinder heads of air-cooled engines (motorcycle, scooter and others) have fins on the outer surface - the presence of fins greatly increases the surface area of the head, ensuring its effective cooling by the oncoming air flow.
Issues of maintenance, repair and replacement of cylinder head
The cylinder head and the components mounted on it are subjected to significant loads, which leads to their intensive wear and breakdown. As a rule, malfunctions of the head itself are infrequent - these are various deformations, cracks, damage due to corrosion, etc. For replacement, you should select a head of the same type and catalog number, otherwise the part simply will not fall into place (without modifications).
Most often, cylinder head breakdowns occur in the systems installed on it - timing, lubrication, etc. Usually this is wear of valve seats and bushings, the valves themselves, drive parts, camshaft, etc. In all these cases, defective parts are replaced or repaired. However, in a garage, some types of repairs are difficult to perform, for example, pressing and pressing the valve guide bushings, lapping valve seats and other work is possible only with a special tool.
Particular attention should be paid to the correct installation of the cylinder head. It is important to remember that the cylinder head gasket is disposable, it must be changed if the head is dismantled, re-installation of this part is unacceptable. When installing the cylinder head, the correct order of tightening fasteners (studs or bolts) should be observed: usually work begins from the middle of the head with movement towards the edges. With this tightening, the load on the head is evenly distributed and unacceptable deformations are prevented.
During the operation of the car, maintenance of the head and the systems located in it should be carried out in accordance with the instructions and recommendations of the manufacturer. With timely maintenance and repair, the cylinder head and the entire engine will work reliably and efficiently.
Post time: Aug-21-2023
