
In internal combustion engines with a belt drive of the gas distribution mechanism, it is necessary to ensure the correct position of the belt and its stabilization during operation. These tasks are solved with the help of bypass rollers, the purpose, design and replacement of which are described in detail in this article.
What is a timing bypass roller?
The bypass (support, intermediate, parasitic) roller is an auxiliary element of the belt drive of the gas distribution mechanism (timing), a free-rotating pulley of small diameter, through which the timing belt is circled at a certain point (or points).
The timing bypass roller solves several problems:
• Changing the belt travel (turning to the required angle) in accordance with the location of the camshaft pulleys and attachments;
• Elimination of vibrations of the belt branches with their considerable length;
• Stabilization of the timing belt during operation, prevention of resonance phenomena, slippage, etc.;
• Overall noise reduction of the gas distribution mechanism.
In the timing belt drive, one bypass roller is usually used, less often two, but many modern small-volume engines do not have these parts at all. At the same time, one should not confuse the bypass roller with another similar mechanism - a tension roller. The tension roller provides the necessary tension of the belt, preventing it from slipping and related engine breakdowns, and also performs the functions of a bypass roller along the way. In the future, we will talk about bypass rollers.
Types and design of timing bypass rollers
Regardless of the type, all bypass rollers are arranged in the same way. The basis of the roller is a bearing, on the outer ring of which a pulley is pressed. The bearing is radial (perceives only loads directed along the radius), ball or roller, can be ordinary single-row or wide double-row. The end face of the bearing can be closed with a metal cover or sleeve to protect against dirt, dust, water and technical fluids. The pulley is stamped metal or solid-cast plastic, non-separable, depending on the type of engine, has a different width and diameter.
Bypass rollers can have a pulley made of various materials:
• Metal – aluminum alloy or steel;
•Plastic.
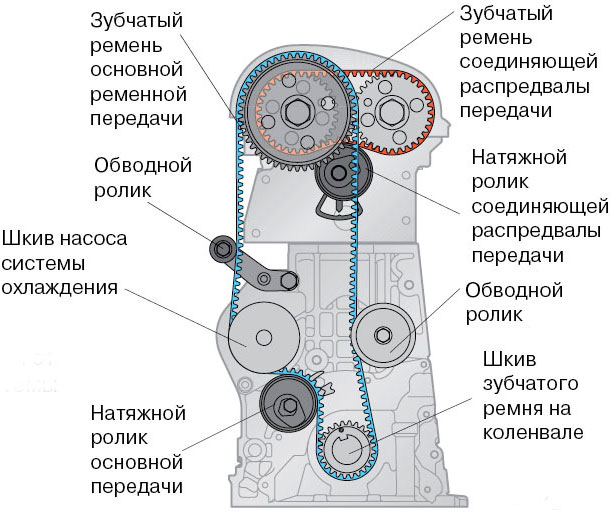
Example of a timing drive with two bypass rollers of different diameters
Currently, plastic rollers are widely used, they are cheaper than metal ones, while providing less noise and reducing the overall weight of the system. Plastic is subject to wear, but the resource of modern plastic bypass rollers is great, they normally serve the entire service interval (between belt replacements).
Metal rollers are used in powerful and highly loaded engines, in which it is important to ensure the reliability of the timing drive in all modes.
Rollers can have pulleys with different types of working surfaces (raceways):
• Smooth – the working surface is smooth, does not have any irregularities;
• Corrugated - the working surface has longitudinal grooves of shallow depth, this design reduces the contact area of the pulley with the belt;
• Toothed - the working surface carries transverse teeth, this is a toothed pulley of free rotation.
At the same time, rollers with a smooth and corrugated pulley can be made of both plastic and metal, and toothed rollers are only metal - steel or aluminum alloys.

Toothed bypass roller
Smooth and grooved rollers are installed in such a way that the belt covers them with its back (smooth) side. Toothed rollers are arranged in such a way that the belt covers them with its working (toothed) side. Replacing rollers of one type with another is unacceptable, as this changes the characteristics of the entire system and is fraught with engine breakdowns.
Finally, bypass roller pulleys, regardless of type, can have two versions:
• Without thrust collars;
• With thrust collars.
In the second case, the pulley on one or both sides has collars of small height that prevent the belt from slipping. On plastic and metal smooth rollers, the collar, as a rule, forms a single unit with the pulley, it is stamped, cast or turned. On toothed rollers, the collar on one or both sides can be made in the form of removable rings, which are mounted when the roller is installed on the engine.
Installation of the bypass roller on the engine is carried out in two ways:
• Directly to the engine block;
• Using a separate bracket.
In the first case, the roller with its bearing rests on a specially provided platform on the engine block and is fixed with one bolt (through a washer of increased diameter). In the second case, the roller is fixed on the bracket, which, in turn, is mounted on the engine block with two or more bolts.
Selection, replacement and operation of timing bypass rollers
Bypass rollers wear out during operation and need to be replaced - this operation is carried out simultaneously with the replacement of the timing belt and the tension roller. All these parts, as a rule, are sold in a kit, so there is no need to look separately for a roller and fasteners for it. When buying a belt and rollers, you should take into account the recommendations of the engine manufacturer and select parts of the appropriate types and catalog numbers.
In some cases, the roller may deteriorate or fail completely. Most often, problems arise in the bearing, in which case extraneous noise appears during engine operation. The roller pulley causes problems much less frequently. In any case, the roller must be replaced, for this you need to purchase a new part according to the manufacturer's instructions and perform work in accordance with the instructions for repair and maintenance of this particular car.
During operation, the bypass roller does not require special maintenance, usually this part works normally throughout the service interval and does not cause problems.
The body and lens of the headlamp are marked with its main characteristics and the types of lamps that can be installed. Installation of other light sources is unacceptable (with rare exceptions), this can change the characteristics of the headlight, and as a result, the vehicle will not pass inspection.
Issues of selection, replacement and operation of car headlights
To choose new optics, it is necessary to take into account the design, features and characteristics of old products, ideally you should buy a headlight of the same model. If we are talking about fog lights or searchlights and searchlights that were not on the car, then here you should take into account the possibility of installing these devices on the car (the presence of appropriate brackets, etc.) and their characteristics.
Special attention should be paid to the choice of headlights. Today, they are usually presented in two versions - with a transparent (white) and yellow segment of the turn signal. When choosing a headlight with a yellow turn signal segment, you need to buy a lamp with a transparent bulb, when choosing a headlight with a white turn signal segment, you need to buy a lamp with a yellow (amber) bulb.
Replacement of headlights is carried out according to the instructions for operation and repair of the car. After replacement, it is necessary to adjust the headlights according to the same instructions. In the simplest case, this work is performed using a screen - a vertical plane with markings on which the headlights are directed, a wall, garage door, fence, etc. can act as a screen.
For European-style low beam (with asymmetric beam), it is necessary to ensure that the upper limit of the horizontal part of the light spot is located just below the center of the headlights. To determine this distance, you can use the following formula:
h = H–(14×L×H)/1000000
where h is the distance from the axis of the headlights to the upper boundary of the spot, H is the distance from the road surface to the center of the headlights, L is the distance from the car to the screen, the unit of measurement is mm.
For adjustment, it is necessary to put the car at a distance of 5-8 meters from the screen, the value h should lie in the range of 35-100 mm, depending on the height of the car and the location of its headlights.
For the high beam, it is necessary to ensure that the center of the light spots lies about half the distance from the optical axis of the headlamp and the border of the low beam light spot. Also, the optical axes of the headlights should be directed strictly forward, without deviations to the sides.
With the right choice and adjustment of headlights, the car will receive high-quality lighting equipment that meets the requirements of standards and ensures safety on the road when driving in the dark.
Post time: Aug-22-2023
