
The wheels of almost all wheeled vehicles, tractors and other equipment are mounted on the hub using threaded studs and nuts. Read about what a wheel nut is, what types of nuts are used today, how they are arranged, as well as their selection, replacement and operation - read in this article.
What is a wheel nut?
Wheel nut (wheel nut) is a threaded fastener for rigid mounting of the wheel on the hub; Nut of special design and shape, optimized for reliable pressing of the rim to the hub.
Nuts are used on vehicles whose wheels are mounted on studs or embedded bolts mounted on the back of the hub. One wheel is fastened with a set of nuts in the amount of four to ten pieces or more. The safety of the car depends to a significant extent on the quality of the nuts and the reliability of their installation, therefore, if even one nut breaks or loses, it must be changed. And in order to make the right choice and replace nuts, you need to understand their design and features.
Types and design of wheel nuts
All wheel nuts, regardless of type, have the same design in principle. In general, this is a hexagonal part with a through central hole or a blind channel in which the thread is cut. The outer part of the nut has a chamfer, the back (adjacent to the disc) is flat, conical, spherical or other, as described below. Additionally, the nuts can be equipped with washers or fixed flanges. Today, nuts are most often made by cold forging from alloy steels, electrolytic anti-corrosion coatings based on zinc, chromium, nickel, cadmium or copper are additionally applied to the products.
Modern wheel nuts differ in design, type of bearing surfaces and applicability.
By design, nuts are of two types:
● Open-threaded (conventional);
● With closed thread (cap).
Products of the first type are ordinary nuts with a through hole in which the thread is cut. Products of the second type are made in the form of caps, inside of which a blind threaded channel is made. Cap wheel nuts protect the thread from negative environmental influences and give an aesthetic appearance to the entire wheel.
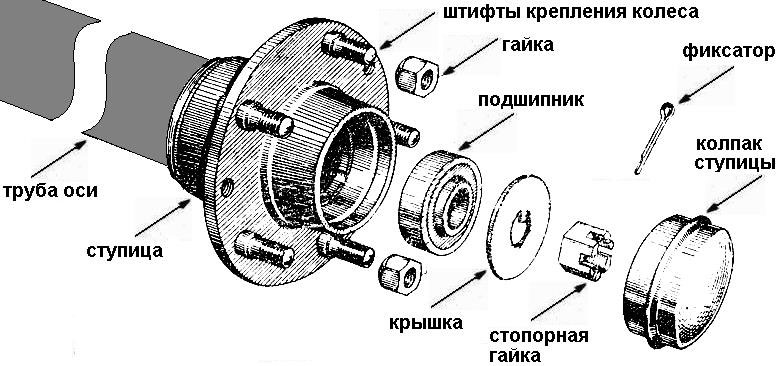
The hub assembly and the place of the wheel nuts in it
In this case, the nuts can have an outer surface for different types of wrench:
● Standard nuts - outer hexagon;
● Non-standard nuts - cap nuts for the inner hexagon, for TORX wrenches and others;
● Nuts for a special wrench ("secrets").
According to the design of the supporting surface of the nut (the surface with which the product rests on the rim during installation, providing its clamping) are divided into four standard types:
● Type A - the supporting surface is made in the form of a spherical flange with a larger diameter than the nut itself. They are divided into type A with M12–M20 thread (reduced height) and type A with M22 thread (increased height);
● Type B - the supporting surface is made in the form of a flat flange of a larger diameter than the nut itself;
● Type C - the supporting surface is made in the form of a truncated cone with a diameter decreasing towards the top;
● Type D - the bearing surface is made in the form of a captive thrust washer with a flat base of a larger diameter than the nut itself.
Cone nuts of the "European" type stand out in a separate category - their bearing surface is made in the form of a conical flange of increased diameter. They are not standardized in Russia, but they are widely used.

Wheel nuts with spherical bearing surface
There are also various non-standard nuts:
● Locking nuts - products with a flat thrust surface, complete with corrugated washers (one or two) that prevent spontaneous unscrewing of fasteners;
● Nuts of increased length - products that have a design similar to standard fasteners, but differ in increased length;
● "Skirts" - nuts with an increased length of the threaded part, used for mounting alloy wheels with deep wells for fasteners;
● Nuts of other shapes.
According to the applicability, wheel nuts are divided into several groups on the side of installation on the vehicle and the possibility of using them with one or another type of rims.
On the side of the installation on the vehicle, the nuts are:
● Universal;
● For the left side (with the "right" thread);
● For the right side (with the "left" thread).
Universal nuts have a normal ("right") thread, they are used to mount all wheels of cars, commercial and many trucks. The same nuts are used to mount the wheels on the left side (in the direction of travel) of trucks, and nuts with a "left" thread hold the wheels on the right side. This use of nuts prevents them from spontaneously unwinding when the vehicle is moving.
Finally, nuts are manufactured for use on various types of rims:
● For stamped discs;
● For cast (alloy wheels) and forged wheels.
Nuts for alloy wheels have an enlarged support surface of a conical or spherical shape, which provides the best load distribution on the disc and prevents its deformation. In addition, today there is a huge variety of special nuts for alloy wheels with various decorative effects, which are widely used in the field of auto-tuning.
Secret nuts
In a separate category, the so-called "secrets" (or nuts for a special turnkey) stand out - nuts of a special design that prevent (or at least reduce the likelihood) of unauthorized unscrewing of nuts and theft of wheels from the vehicle. As a rule, one secret is installed on the wheel instead of one of the standard nuts, so a set of four or six (depending on the number of axles) of such products is enough for the car.
All secrets have one principle - these are smooth nuts that can be tightened and unscrewed only with the help of a special wrench that comes with the kit. In the simplest case, protection is provided by a complex (not hexagonal) shape of the outer surface of the nut, the most advanced secrets have a hidden turnkey surface and protection against unscrewing with pliers (outer cone, outer swivel surface, and others).
According to the characteristics, the secrets are identical to conventional wheel nuts.
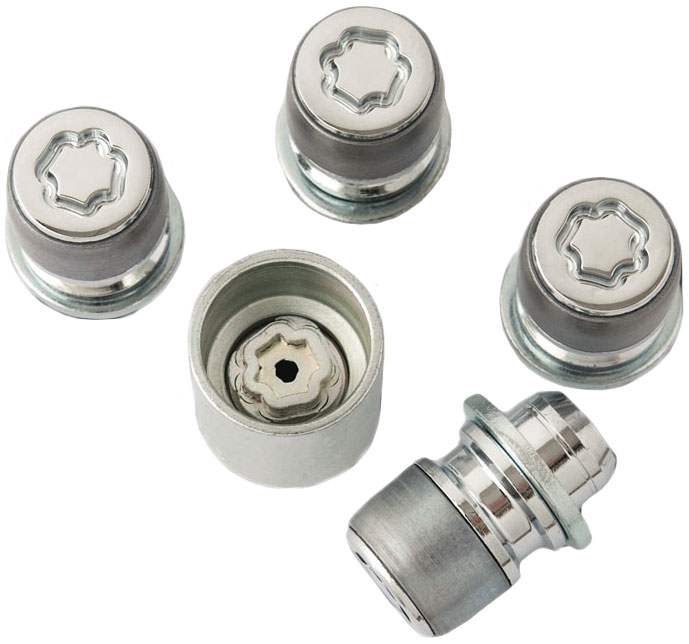

Secret nuts complete with a special wrench
Characteristics of wheel nuts
Of the main characteristics of wheel nuts can be distinguished:
● The size and direction of the thread;
● Turnkey size;
● Strength class.
Type A, B and C nuts are available in six thread sizes – M12 with fine threads (with a pitch of 1.25 mm), M12, M14, M18, M20 and M22 with a thread pitch of 1.5 mm. Type D nuts designed for trucks have a thread of M18, M20 and M22 with a pitch of 1.5 mm. Accordingly, the turnkey size of wheel nuts can be 17, 19, 24, 27, 30 and 32.
Nuts to ensure reliability and the possibility of tightening with the necessary force without deformation must have a strength class of 8 or 10 (and nuts with a captive support washer - at least 10). This is achieved by the use of certain grades of steel and (sometimes) additional processing of the finished product.
All wheel nuts produced in Russia in terms of design and characteristics must comply with the requirements of GOST R 53819-2010 and a number of other related standards. Many foreign automakers use their own standards for fasteners, so their nuts may differ in design from those described above.
Proper selection and replacement of wheel nuts
Over time, wheel nuts deform, become less durable, or simply lost if installed incorrectly - in all these situations, it is necessary to install new fasteners. For replacement, it is necessary to choose nuts of the same type and with the same characteristics that were installed earlier - this is the only way the fasteners are guaranteed to fit.
If the rims were replaced, then the nuts must be selected for them. So, together with conventional steel stamped discs, standard conical, spherical or flat nuts are used. With truck discs (including Euro wheels), nuts with a captive thrust washer have recently been increasingly used. And for alloy wheels, you should choose the appropriate nuts with an enlarged bearing surface or special nuts.
Particular attention should be paid to the choice of nuts for trucks - here it should always be remembered that on the right side the discs are fastened with nuts with a left thread.
Care should be taken to choose nuts for tuning a car. Today, the market offers a huge variety of fasteners for alloy wheels, but often these nuts do not meet the standards for strength and other characteristics - this is fraught with breakage of fasteners and accidents.
When installing the wheel, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the automaker for tightening the nuts - take into account the sequence and tightening force. As a rule, the nuts are tightened crosswise with such a force that would ensure a reliable fastening of the wheel and would not deform the disc. With a weak tightening, spontaneous unscrewing of the nuts is possible, and intensive wear of the studs and holes of the rim also occurs. Excessive tightening can cause deformation of the disc and increase the likelihood of cracks and other damage.
Only with the correct selection and installation of wheel nuts, the car will be stable on the road and safe in various situations.
Post time: Aug-05-2023
